High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA)
From Computing and Software Wiki
(→Technology) |
m (→Technology) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
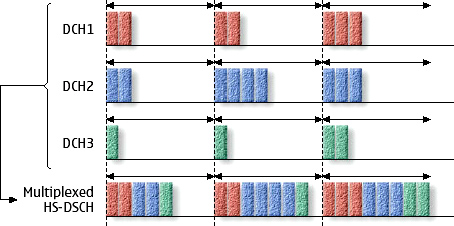
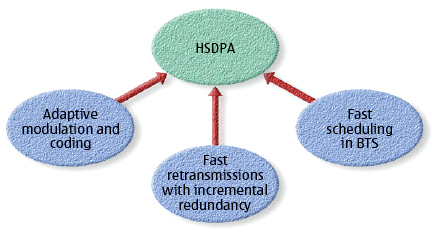
High Speed Downlink Packet Access technology is based on [[Universal Mobile Telecommunications System]] [UMTS] standard that enhances the capabilities of 3G by enabling higher data transfer rates. Since HSDPA is using [[High Speed Downlink Shared Channel]], it has two weak points; variavle spreading factor and fast power control. Therefore, HSDPA implementations includes Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO), Hybrid Automatic Request (HARQ), fast cell search, Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC), and advanced receiver design. | High Speed Downlink Packet Access technology is based on [[Universal Mobile Telecommunications System]] [UMTS] standard that enhances the capabilities of 3G by enabling higher data transfer rates. Since HSDPA is using [[High Speed Downlink Shared Channel]], it has two weak points; variavle spreading factor and fast power control. Therefore, HSDPA implementations includes Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO), Hybrid Automatic Request (HARQ), fast cell search, Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC), and advanced receiver design. | ||
| - | [[Image:HSDPA_Share.jpg]] | + | [[Image:HSDPA_Share.jpg]] [[Image:HSDPA_Structure.jpg]] |
=== Multiple-Input Multiple-Output === | === Multiple-Input Multiple-Output === | ||
Revision as of 07:27, 12 April 2009
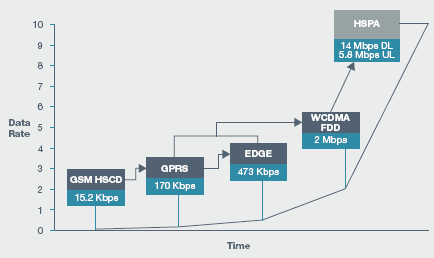
High Speed Downlonk Packet Access is a 3.5G [G stands for generation] technology. HSDPA, short for High Speed Downlink Package Access is a new new mobile telephony protocol, which allows to have high data speed transmission and large amounts of capacity. It will provide download speed on a mobile phone same as an Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line [ADSL]. HSDPA can archieve data transmission Speed of 8-10 Mbit/s. For future improvement, HSDPA provides up to 42Mbit/s data transmission speed.
Contents |
Technology
High Speed Downlink Packet Access technology is based on Universal Mobile Telecommunications System [UMTS] standard that enhances the capabilities of 3G by enabling higher data transfer rates. Since HSDPA is using High Speed Downlink Shared Channel, it has two weak points; variavle spreading factor and fast power control. Therefore, HSDPA implementations includes Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO), Hybrid Automatic Request (HARQ), fast cell search, Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC), and advanced receiver design.
Multiple-Input Multiple-Output
Adaptive Modulation and Coding
Hybrid Automatic Request
Packet Scheduling
Usage
Testing
Comparison
orz