Steganography and Digital Watermarking
From Computing and Software Wiki
Steganography and Digital Watermarking are both forms of information hiding where the context can be viewed as keeping the information a secret or making the information subtle respectively. Both these methods have been around for a long time, at least several centuries, however they have only gained worldwide popularity in the digital world since roughly the mid 1990s. With new technologies constantly emerging, these two methods have been used to prevent theft, prevent plagiarism, track, and hide secrets among other things. There is not one standard way of implementing these techniques and each version differs from one another. Thus, with the vast amount of applications these techniques can be applied to, many companies have made software to create and detect both techniques.
Contents |
What is Steganography?
Steganography is the method of concealing the message and its very existance is a secret and only known to the person(s) who placed it.
What is Digital Watermarking?
History
The word steganography was derived from the Greek words steganos, which means "covered", and graphia, which means "writing". The first recorded entry of the use of steganography is in the story of Herodotus and his slaves. Where he shaved the heads of his slaves and tattooed secret messages on their scalps. He would than let their hair grow back to hide the message and send his slaves to deliver the messages to other leaders. Since than, many early proposed steganographic techniques have been created from hiding messages in jewellery, to modifying letter strokes and sizes, and placing a mask over text. Many of these techniques are still used today and were used during World War I and II.
Other techniques that were more sophisticated that were used as well during the wars were microdots, which were microscopic images that were shrunk to resemble tiny specs of dirt. These microdots were placed on a person or in a letter and were used to transmit vital information or locations. From this moment and with the emergence of the Internet, steganographic techniques began increasing. Due to the amount of computer networks and digitalized media, covert steganography became favourable to communicate between parties. There have been many uses of steganography, good and bad, in which they provide an extra layer of security for businesses but could also be used by criminals for illegal means.
The word watermark is thought to have been derived from the German word wassermarke and is termed as the marks were thought to have resembled the effects of water on paper. Watermarking first began in Italy in 1282 where wired patterns were created during paper production which left
designs in the paper once it molded. The purpose is unclear as to why watermarking was done back
than. However in the eighteenth century, paper made in Europe and America using watermarking
technology was to ensure trademarks, track when the paper was created, indicate size of the
sheets, and prevent counterfeiting.
Counterfeiting especially, caused watermarking technolgy to rapidly increase as there were those attempting to stop counterfeiters and those attempting to remove or copy the watermarks. From the basic imprints on paper, watermarks moved onto colour where dyed ink was inserted into the paper during the molding process. The next advancement was to create a raise in the paper causing a slight bump on the surface, which is commonly seen on paper currency today. Finally, the idea of digital watermarking appeared between in 1979, where Szepanski discussed a machine that could be used on documents which would place a pattern for anti-counterfeiting purposes. In 1988, Holt described a way of embedding an identification code in an audio signal and the term digital watermark first appeared. It was only until 1995 that the world became vastly interested in the idea of digital watermarks. From then on, many papers were released discussing ways of implementing digital watermarks and companies ranging from the music industry to business software began using this technique for security and protection.
Applications
Steganography and digital watermarking can be broken down into four different subcategories in which the existence of the technique is either known or unknown to the public along with the original file.

Covert watermarking is embedding a watermark related to the recipient of each copy of the file, but unaware that the watermark exists. Thus, if the file is leaked to third parties, the recipient who leaked the file can be traced. Covert steganography is embedding data unrelated to the original work. An overt watermark is when the presence of the watermark is known to others besides the creators, whether visually or told of the watermark. Overt steganography is similar to covert steganography in terms of the hidden information is unrelated to the signal in which it is embedded in. However with overt steganography, the information is only hidden to certain parties but visible to others, example timestamps.
Knowing the subcategories allows for the following possible applications for both steganography and digital watermarking. Some applications may use both techniques depending on the function required.
Steganography
Some applications of steganography are:
- Protection of Data Alteration
- Confidential Communication
- Media Database Systems
- Access Control
Digital Watermarking
Some applications that use digital watermarking are:
- Broadcast Monitoring
- Owner Identification
- Proof of Ownership
- Transaction Tracking
- Content Authentication
- Copy Control
- Device Control
- Legacy Enhancement
Properties
Properties of Steganographic Systems
Some properties of steganography are:
- Robustness
- Security
- Embedding Effectiveness
- Fidelity
- Steganographic Capacity
- Blind or Informed Extraction
- Embedding Capacity
- Embedding Efficiency
- Data Payload
- Blind or Targeted Steganalysis
- Statistical Undetectability
- False Alarm Rate
- Stego Key
Properties of Watermarked Systems
Some properties of digital watermarking are:
- Robustness
- Security
- Embedding Effectiveness
- Fidelity
- Data Payload
- Cipher andWatermark Keys
- Blind or Informed Detection
- False Positive Rate
- Modification and MultipleWatermarks
- Cost
Models and Techniques
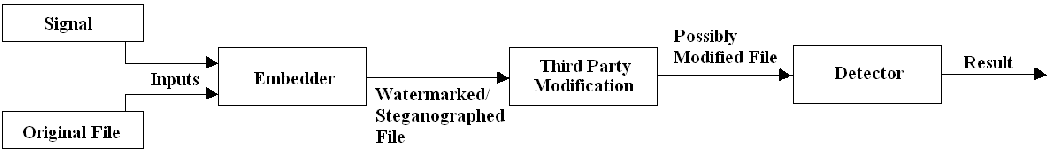
Steganography and digital watermarking are two different techniques, however they both share similar qualities. Both techniques follows the same basic model in which two inputs (a signal and the original file) go into an embedder. The signal corresponds to the digital watermark or the secret message and the embedder function contains an algorithm that will produce a watermaked file. The output from the embedder is than transmitted or recorded. The recorded file is than sent to a third party in which the possibility of a modification, whether malicous or not, could arise. The recorded file, modified or not, is than sent as input to a detector in which the algorithm tries to determine if the signal is present. If it is, the watermark or secret message can usually be extracted depending on the properties.
How Steganography Works
How Digital Watermarking Works
Countermeasures
Countermeasures or detection techniques against covert steganography or watermarking requires the use of the light spectrum, magnification lenses, chemical mixtures, cipher algorithms, and others are used to determine if a file has been embedded with either these techniques.
References
See Also
- Cryptography in Information Security
- Public Key Authentication
- Corporate Security and IT Policies
- CAPTCHA
- Personal Data Protection and Privacy
- MD5 Rainbow Tables
- Data Encryption for Storage Devices
- Conventional Encryption Algorithms
- Information security awareness
- Digital Signatures
- Statistics of Internet Threats
- Multicasting
External Links
- Steganography Revealed
- Hide and Seek: An Introduction to Steganography
- Steganography Tools
- Steganography and Steganalysis
- Robustness and Security of Digital Watermarks
- On the Limitations of Digital Watermarks: A Cautionary Note
- Digital Watermarking Alliance
- Digital Watermarking World
--Ganv 20:14, 7 April 2009 (EDT)