Personal Data Protection and Privacy
From Computing and Software Wiki
Personal data are a set of data such as name, social insurance number, birthday dates, credit card number etc that needs to be kept secure. These data can be stolen if a computer is connected to the internet and the information is on the computer. A lot of hackers on the internet use their computer or other people’s computer to gain access into your computer to steal personal information that they then use for malicious purposes. Hackers have free access to a computer when there is a security hole in the software or operating systems that are being used on your computer.
Contents |
Possible threats to Personal Data
Pharming – This is done by directing an internet user to a different site than the one requested. This is done by changing the DNS and IP address of the target website from the original IP address to the IP address of the mirrored website. Therefore whenever the user tries to access the original site, the user is directed to the mirrored website. This form of attack is very difficult for the user to realize unless the user checks the SSL certificates and is realizes that it is a fake certificate.
Phishing – This is the process of trying to acquire personal information from an individual by pretending to be an organization that they are not. Phishing can occur through email when a message is sent requesting for information such as birth date, social insurance number and PIN numbers. Also mirror websites could be created to look like the authentic website. Information such as the user ID and password would be requested hereby gaining access to the account of the user.
Spear Phishing – This occurs when spear phishers disguises as friends of an individual on a social networking site such as Myspace and Facebook to develop trust with an individual. When trust has been developed with an individual, then the spear phishers gets personal information through message boards and personal messages. The information collected can be used for malicious purposes.
Vishing – Emails are sent to individuals stating that there is some problem with their credit card and then they are asked to either click on a link or call a specific number where the credit card number, expiry date and verification codes are collected from the users. This information is then used to incur fraudulent charges on the user’s card.
How to Protect Personal Data
Using Firewalls
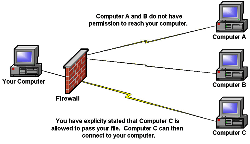
A firewall is a collection of security measures designed to prevent unauthorized access to a networked computer. It blocks all internet traffic that is not being specifically specified by the computer from coming to the computer. There are two types of firewalls that can be used depending on the computer that needs to be secured.
Hardware Firewall
This is a device that allows the connection of different computers to a hub. The firewall monitors requests that are coming from the internet into the computers connected to the hub. This type of firewall protection is mainly used by organizations that need to control the information being sent to out of the organization and information received from other sites.
Personal Firewall
A personal firewall is a software installed on each computer that needs to be protected. A personal firewall has more features than a hardware firewall but the software cannot be shared with different computers.
Email Authentication
Emails are received from financial institutions, internet service providers and other organizations requesting for personal information. This information should not be released through email without authenticating the source of the email. The most secure method of doing this is by calling the organization and verifying that they require this information.
Providing Personal Data on the web
When providing personal information or data on the internet, ensure that the web site is authentic. A good way of checking that the web site is authentic is by typing in the web address manually.
Privacy Law governing release of Personal Data
In Canada, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act] (PIPEDA) governs organizations on the collection, use and disclosure of personal data during commercial interaction. This law does not allow the release of personal information to third party organization except when the consent of the owner has being received. There are some exceptions to this law, an example is when the information is needed for law enforcement.
The law gives individuals the right to
- know why an organization collects, uses or discloses their personal information;
- expect an organization to collect, use or disclose their personal information reasonably and appropriately, and not use the information for any purpose other than that to which they have consented;
- know who in the organization is responsible for protecting their personal information;
- expect an organization to protect their personal information by taking appropriate security measures;
- expect the personal information an organization holds about them to be accurate, complete and up-to-date;
- obtain access to their personal information and ask for corrections if necessary; and
- complain about how an organization handles their personal information if they feel their privacy rights have not been respected.
The law requires organizations to
- obtain consent when they collect, use or disclose their personal information;
- supply an individual with a product or a service even if they refuse consent for the collection, use or disclosure of your personal information unless that information is essential to the transaction;
- collect information by fair and lawful means; and
- have personal information policies that are clear, understandable and readily available.
References
- Bleeping Computer. 2004. Firewalls
- East Carolina University. 2008 Guidelines for Protecting Sensitive Data
- Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada. 2007. Recognizing Threats to Personal Data
- Wikipedia. 2009. Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act
See also
Systems for Detecting Network Intrusion
External links
How To Protect A Company's Data
13 ways to protect personal data from online fraud and identity theft
--Komolat 21:13, 12 April 2009 (EDT)