High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA)
From Computing and Software Wiki
m (High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) moved to High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA): Purpose of direct link) |
m (→References) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| - | == | + | == External Links == |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 23:58, 12 April 2009
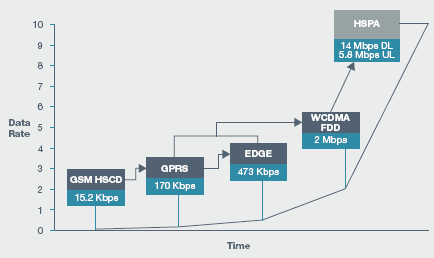
High Speed Downlonk Packet Access is a 3.5G [G stands for generation] technology. HSDPA, short for High Speed Downlink Package Access is a new new mobile telephony protocol, which allows to have high data speed transmission and large amounts of capacity. It will provide download speed on a mobile phone same as an Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line [ADSL]. HSDPA can archieve data transmission Speed of 8-10 Mbit/s. For future improvement, HSDPA provides up to 42Mbit/s data transmission speed.
Contents |
Technology
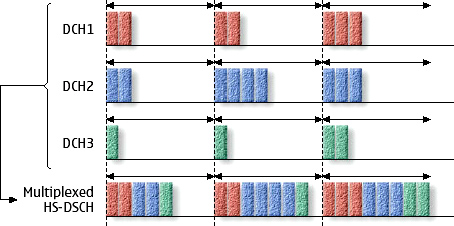
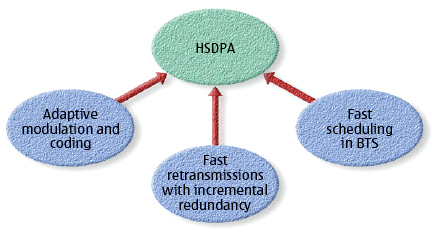
High Speed Downlink Packet Access technology is based on Universal Mobile Telecommunications System [UMTS] standard that enhances the capabilities of 3G by enabling higher data transfer rates. Since HSDPA is using High Speed Downlink Shared Channel, it has two weak points; variavle spreading factor and fast power control. Therefore, HSDPA implementations includes Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO), Hybrid Automatic Request (HARQ), fast cell search, Adaptive Modulation and Coding (AMC), and advanced receiver design.
Multiple-Input Multiple-Output
This technology is using more than one antenna to send and receive multiple data streams over the same channel simultaneously in wireless devices, therefore it gives long ranges and high throguhputs in network. This is based on 802.11n wireless transmission standard and it can reach more than 300 feet and still send and receive ddata at 30mbps.
Adaptive Modulation and Coding
Adaptive Modulation and Coding provides the flexibility to match the modulation coding scheme to the regular channel condition for each user. Therefore, the power of the transmitted signal treats as constant over a frame interval, and the format of modulation and coding is automatically matched to the current received signal or channel conditions.
Hybrid Automatic Request
After first transimission in HSDPA, there are 10% to 20% of error rate. Therefore, the Hybrid Automatic Request (HARQ) mechanism is helped to reduce the delay and increase the efficiency of retansmitting data. Therefore even if a error packet is received, it will combinate with the retransmissions, to have error-free packet.
Packet Scheduling
In HSDPA, the packet scheduling is located in the medium access layer, MAC-hs. The MAC-hs is located in the Node-B, therefore packet scheduling decisions are almost instantaneously executed. With large AMC dynamic range with the HSDPA, the channel allocation is conducted to the most popular packet scheduling method; radio conditions. With this scheduler, the order is determined by the highest instantaneous relative channel quality.
Usage
There are many products that are already using HSDPA technology. The mainly mobile
Comparison
orz
See Also
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line