VoIP
From Computing and Software Wiki
m (→Analog Telephone Adapter) |
m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Types of VoIP Calls= | =Types of VoIP Calls= | ||
| - | '''Analog Telephone Adapter | + | The '''Analog Telephone Adapter''' is a device used to connect a standard analog telephone to a computer network so that the user can make voice calls over the internet. ATA devices usually come in two forms. In a household setting, it usually has one or more RJ-11 jacks to connect to a telephone and a USB connector to connect to a computer, laptop or hand-held device. This type of ATA requires the service of computer software to digitize voice data and communicate with the VoIP server. In an enterprise setting, the ATA usually consists of multiple telephone jacks and an RJ-45 connector to connect to an Ethernet hub or switch. This type of ATA contains its own analog to digital converters and uses protocols such as H.323 and SUO to communicate with the VoIP server. |
| - | + | '''VoIP Phones''' are specialized phones that allow a direct connection to the IP Network via Ethernet of Wi-Fi technology. Therefore, they allow the use of VoIP without the use of computer. There are two types of VoIP Phones: IP Phones and Wi-Fi phones. IP Phones have a different connector than regular phones. This connector (RJ-45 connector) allows it to link directly with the router via an Ethernet cable. Wi-Fi phones allow the VoIP calls with connection from any Wi-Fi hotspot. The Cisco IP Phone is a common example that is used in many companies. | |
| - | + | A '''Softphones''' is VoIP software is installed on a computer and is used in conjunction with the computers microphone, speaker, sound card and internet connection. Skype is a common example of Computer-to-Computer VoIP technology. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 8 April 2009
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a general term for a family of technologies that convert analog audio signals (voice) to digital data that is then transmitted over IP networks such as the Internet or other packet switched networks. VoIP technology is sometimes also called IP telephone, Internet telephony, voice over broadband (VoBB), broadband telephone and broadband phone. The major benefits arising from VoIP technology is the reduction in communication and infrastructure costs. Routing phone calls over existing data networks eliminate the need for creating separate data and voice networks. This reduces the infrastructure costs of companies. VoIP features such as conference calling and caller ID which usually cost extra with most telecommunication companies are available for free with most VoIP services. The average consumer can eliminate long distance charges altogether by using a service such as Skype to communicate with relatives.
Contents |
Types of VoIP Calls
The Analog Telephone Adapter is a device used to connect a standard analog telephone to a computer network so that the user can make voice calls over the internet. ATA devices usually come in two forms. In a household setting, it usually has one or more RJ-11 jacks to connect to a telephone and a USB connector to connect to a computer, laptop or hand-held device. This type of ATA requires the service of computer software to digitize voice data and communicate with the VoIP server. In an enterprise setting, the ATA usually consists of multiple telephone jacks and an RJ-45 connector to connect to an Ethernet hub or switch. This type of ATA contains its own analog to digital converters and uses protocols such as H.323 and SUO to communicate with the VoIP server.
VoIP Phones are specialized phones that allow a direct connection to the IP Network via Ethernet of Wi-Fi technology. Therefore, they allow the use of VoIP without the use of computer. There are two types of VoIP Phones: IP Phones and Wi-Fi phones. IP Phones have a different connector than regular phones. This connector (RJ-45 connector) allows it to link directly with the router via an Ethernet cable. Wi-Fi phones allow the VoIP calls with connection from any Wi-Fi hotspot. The Cisco IP Phone is a common example that is used in many companies.
A Softphones is VoIP software is installed on a computer and is used in conjunction with the computers microphone, speaker, sound card and internet connection. Skype is a common example of Computer-to-Computer VoIP technology.
How Does VoIP Work
Stages of VoIP transmission
- First the analog voice must be converted to a digital signal via an analog-to-digital converter
- The digital signal must be compressed for transmission
- The voice packets are then inserted into data packets using a real-time protocol (RTP)
- A signaling protocol is then required to call a user
- When the packet reaches the destination it must be disassembled
- The data is then extracted or decompressed
- The digital signal is then converted back to an analog voice signal via a digital to analog converter
Analog to Digital Conversion
Two factors play an important role in the successful digitization of an analog voice signal:
- Quantization: This refers the number of bits used to represent each sample. Audio signals are best represented by 16 bit samples.
- Sampling rate: This refers to the number of samples per second used to encode the sound. 8 kHz is the most common sampling frequency used to VoIP communication.
Real Time Protocol
After the data is converted into the correct format it is encapsulated in RTP Packets to be transmitted over the network. This transmission protocol needs to consider the following situations:
- The re-ordering of packets during the transmission
- The loss of packets
- The time between packet arrival (jitter)
For real time transmission, the re-ordering and jitter issues are more important than the loss of packets. It does not matter if a few packets are lost as long as most of them arrive continuously and in order. Therefore, the error checking and retransmission scheme of TCP is not really suitable for this purpose. UDP provides the high speeds required for real time transmission.
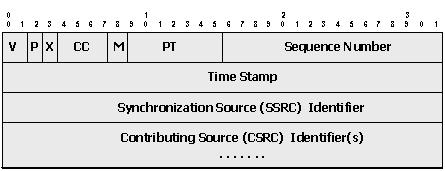
The fields of the RTP packet relevant to VoIP transmission include:
PT (Payload Type): This is a 7 bit field that allows values between 0 and 127. The interval between 96 and 127 is reserved for dynamic payload types. These are negotiated by the signaling protocol (SIPR or H.323) used to establish the VoIP call.
Sequence Number: This is a 16 bit value that helps order the packets after transmission. The sequence number starts at a random value and is incremented with each RTP packet sent
Timestamp: This is a 32 bit value that represents the clock tick count when the first audio sample in the payload was sampled. The timestamp also starts at a random value and incremented with each RTP packet sent.
Synchronization Source Identifier (SSRC): This is a 32 bit identifier that is chosen randomly and used to detect and resolve collisions. No two synchronization sources within the same RTP session will have the same SSRC.