Streaming Media Technology
From Computing and Software Wiki
(→Introduction) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
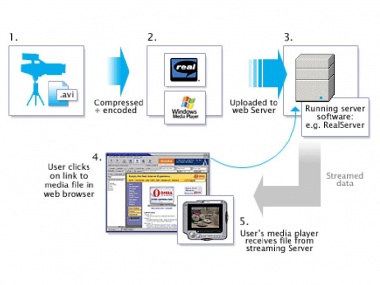
| - | When the user requests to | + | When the user requests to play a media object that is stored on a remote server, the data blocks are retrieved from the remote server over a network, and passes to the client for display. [3] There are ususaly two ways of doing that. First, the media object is completely downloaded from the sever before the display begins. Second, the player can start to play |
== System Architecture == | == System Architecture == | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
[2] Sequence website, "http://www.sequence.co.uk/services/streamingmedia/howdoesitwork.html" . | [2] Sequence website, "http://www.sequence.co.uk/services/streamingmedia/howdoesitwork.html" . | ||
| + | |||
| + | [3] Dashti, Ali E. ''Streaming Media Server Design'', Prentice Hall, 2003 | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 00:31, 9 April 2008
Streaming media is multimedia that is constantly received by, and normally displayed to, the end-user while it is being delivered by the provider.[1] Streaming media technolgy enables on-demand or real-time access to multimedia content via internet and allows users to play those contents without fully downloading them. After playing, there's no copy of played contents leaving on the receiving devices, which protects the copyright of the original mutimedia contents.
Contents |
Introduction
When the user requests to play a media object that is stored on a remote server, the data blocks are retrieved from the remote server over a network, and passes to the client for display. [3] There are ususaly two ways of doing that. First, the media object is completely downloaded from the sever before the display begins. Second, the player can start to play
System Architecture
To be filled
Storage and Bandwidth
To be filled
Data Compression
Run-length encoding
Relative encoding
Huffman encoding
Transform encoding
To be filled
Network Protocols
RTP
RTCP
RTSP
RSVP
To be filled
Applications
- A
- B
- C
- D
References
[1] Wikipedia, "Streaming Media", April 2008, "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Streaming_media" .
[2] Sequence website, "http://www.sequence.co.uk/services/streamingmedia/howdoesitwork.html" .
[3] Dashti, Ali E. Streaming Media Server Design, Prentice Hall, 2003
See also
External links
- streamingmedia.com - Streaming Media Industry News
- Streaming Media - Streaming Media Wiki Page
- TCP/IP_model - Protocols on the Five-layer TCP/IP Model
--Chuh 15:58, 7 April 2008 (EDT)