Operating Systems Security
From Computing and Software Wiki
(→Windows Security Features) |
(→Windows Security Features) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Windows Security Features== | ==Windows Security Features== | ||
Vista, will be the focus here since it is the newest. Some of the more major security features include the following: | Vista, will be the focus here since it is the newest. Some of the more major security features include the following: | ||
| - | + | *User Account Control | |
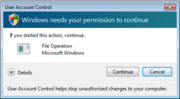
[[Image:180px-User_Account_Control_administrator_dialog.png|frame|An example of User Account Control]] | [[Image:180px-User_Account_Control_administrator_dialog.png|frame|An example of User Account Control]] | ||
Each time the something occurs that may affect the systems security, a prompt will appear that asks whether or not it should be allowed. | Each time the something occurs that may affect the systems security, a prompt will appear that asks whether or not it should be allowed. | ||
| - | + | *Address Space Randomization | |
Many hacker exploits involve overflows into other portions of system memory in order to manipulate certain pieces of code. Vista has randomized memory in order to prevent this. By having memory more scattered, overflows often will not modify the correct address in memory, thereby preventing an exploit. | Many hacker exploits involve overflows into other portions of system memory in order to manipulate certain pieces of code. Vista has randomized memory in order to prevent this. By having memory more scattered, overflows often will not modify the correct address in memory, thereby preventing an exploit. | ||
| - | + | *Integrity-Level Access | |
Everything that is running in Vista is given a certain trust level. For example, something with lower trust cannot modify something with a higher trust level, but something with higher trust may be able to modify something with a lower trust level. | Everything that is running in Vista is given a certain trust level. For example, something with lower trust cannot modify something with a higher trust level, but something with higher trust may be able to modify something with a lower trust level. | ||
| - | + | *Improved Firewall and Address Stack | |
Some updates and improvements from the XP firewall and network security. | Some updates and improvements from the XP firewall and network security. | ||
Revision as of 06:09, 3 December 2007
The security of operating systems has always been a concern for users, and especially so with the invention of the Internet. Operating system developers are constantly creating new ways to protect computers from hackers. The three most common operating systems are Linux, Mac OS and Windows. They each have a different set of security features. So the question is, which is the most secure?
Contents |
Hacking
Hacking is the act of manipulating computers to get them to do exactly what you want. A hacker is the person who does the hacking. A hacker is generally defined as someone who is very good with computers and programming. However, in popular culture, a hacker is considered someone who attempts to break into computer systems. For the purposes of this article, the latter definition will be used. Hacking is done for many reasons, including anything from theft and denial of service to someone hacking because they have a psychological need to do it. It is therefore vital for an operating system to be as secure as possible to protect against them.
Techniques
There are many ways a hacker can attack a system. Some of these include exploits, which take advantage of faulty operating systems coding, or Trojan horses, which are programs that seem to provide one function but actually do something completely different. To get a better understanding of hacking, visit the hacking wiki at Wikipedia.
Common Operating Systems
Windows
There are two releases currently in use today. Windows XP, released in 2001, is currently on 79.07% of all personal computers in the world. Windows Vista, released in 2006-2007, has a market share of 7.97%. Windows provides a fairly straightforward system that is useful to a beginner and a more advanced user. It is a closed source operating system, so only the developers have access to the source code of Windows.
Mac OS
The most recent release is the Mac OS X. It is very different from the original Mac OS, having an improved GUI and many more features. Its market share is estimated to be from 6% to 13% in the personal computing market. It is also meant to be easy to use and also have advanced features. It is a mainly closed source operating system but some major components are open source.
Linux
Linux, in general, is a more advanced operating system. Although it often has a point-and-click interface, some things must be done via a command line, making it slightly harder to use. For this and several other reasons, this operating system is better suited for someone more knowledgeable in computers. It is a completely open-source operating system, meaning anyone can view the source code. It also has many different distributions. Each distribution focuses on different features such as speed, ease-of-use or security. The Linux market share is approximately 1%.
Windows Security Features
Vista, will be the focus here since it is the newest. Some of the more major security features include the following:
- User Account Control
Each time the something occurs that may affect the systems security, a prompt will appear that asks whether or not it should be allowed.
- Address Space Randomization
Many hacker exploits involve overflows into other portions of system memory in order to manipulate certain pieces of code. Vista has randomized memory in order to prevent this. By having memory more scattered, overflows often will not modify the correct address in memory, thereby preventing an exploit.
- Integrity-Level Access
Everything that is running in Vista is given a certain trust level. For example, something with lower trust cannot modify something with a higher trust level, but something with higher trust may be able to modify something with a lower trust level.
- Improved Firewall and Address Stack
Some updates and improvements from the XP firewall and network security.
Mac OS X Security Features
Mac OS X Leopard is the most recent release of Mac OS X. Some of its major features are:
Open Source
Since a portion of the operating system is open source, faults in the code can be found by anyone. This means patches can be found much faster than if the developers were the only ones allowed to view the source code.
Sandboxing
Gives programs as few resources as possible so as to prevent the program from gaining access to vital areas of the system.
File Tagging and Signed Applications
If a program has not been run before, it is tagged. The first time it is opened, the user is asked if the file is OK to be run. Signed applications are ones that have a digital signature. These help identify the integrity and trustworthiness of the program.
Library Randomization
Same idea as the Windows address space randomization, this helps protect against exploits.
Linux Security Features
The number of Linux security features differs with each distribution. Some of the most notable general features are:
SELinux
Provides mandatory access control and integrity checking of programs and processes.
Open Source
Being open source gives Linux a major advantage security-wise. Instead of just developers fixing bugs, all users are capable of this. Studies have shown that many more bugs are found and fixed in open source software than in closed source software.
Stack Smash Protection, Buffer Overflow Detection, Exec-Shield
All of these are systems to prevent exploits. Exec-Shield provides address space randomization, while the others are specific features designed to detect specific exploits.