Multicasting
From Computing and Software Wiki
m (→Broadcast) |
(→Different Types of IP Addressing) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
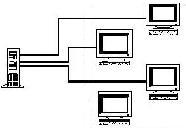
[[Image:Unicast.jpg|frame|This diagram shows the waste of bandwidth and increase in network traffic that is inherent when using Unicast addressing to send the same data to multiple recipients.]]Unicast addressing is the most common form of sending datagrams to other hosts on a network. It refers to sending information packets from one point to another point(one-to-one connection). Some applications that use unicast addressing are http and ftp, among others. | [[Image:Unicast.jpg|frame|This diagram shows the waste of bandwidth and increase in network traffic that is inherent when using Unicast addressing to send the same data to multiple recipients.]]Unicast addressing is the most common form of sending datagrams to other hosts on a network. It refers to sending information packets from one point to another point(one-to-one connection). Some applications that use unicast addressing are http and ftp, among others. | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
===Broadcast=== | ===Broadcast=== | ||
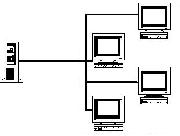
[[Image:Broadcast.jpg|frame|This diagram shows how broadcasting improves the bandwidth trouble unicasting has but still yields a high amount of network traffic.]]Broadcasting is the type of IP addressing where the sender will send a piece of data to all nodes connected to a network. While only one piece of data is being sent, there is no control over who receives it, and so this will place a huge strain on any network. | [[Image:Broadcast.jpg|frame|This diagram shows how broadcasting improves the bandwidth trouble unicasting has but still yields a high amount of network traffic.]]Broadcasting is the type of IP addressing where the sender will send a piece of data to all nodes connected to a network. While only one piece of data is being sent, there is no control over who receives it, and so this will place a huge strain on any network. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Multicast=== | ||
| + | As stated earlier, multicasting is the addressing type that allows a piece of data to be sent once but received by multiple users. It is still relatively new and has some downsides, but compared to the broadcasting and unicasting methods of transmitting data to larges amount of recipients it is far more efficient. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===Anycast=== | ===Anycast=== | ||
Revision as of 19:43, 11 April 2009
Multicasting is a type of internet addressing system where only interested receivers are sent the requested information. This was created to be a more efficient means of broadcasting where information would be sent to every node in the network. Multicasting uses the most efficient routes to transfer the data and only copies the information being sent when a fork in the route occurs. Prior to multicasting, if a user needed to send the same data to N users, the user would need to copy that data N times and send it to each receiver. This creates a high amount of strain on servers, as well as large amounts of traffic over the network. Multicasting however needs only one transmission of this data, and will optimize the path that the data takes to reach each desired user.
Contents |
Different Types of IP Addressing
Unicast
Broadcast
Multicast
As stated earlier, multicasting is the addressing type that allows a piece of data to be sent once but received by multiple users. It is still relatively new and has some downsides, but compared to the broadcasting and unicasting methods of transmitting data to larges amount of recipients it is far more efficient.
Anycast
In the anycast IP addressing scheme, the closest appropriate server is located and the packet is sent to it. The appropriate server will offer a service that the client needs, and so if multiple servers offer this same service, the packet can go to 'any' of these servers(however the closest server is deemed the most appropriate). This is where the name anycasting is derived from. Anycasting is advantageous because it simplifies the task of locating servers.