Domain Name System
From Computing and Software Wiki
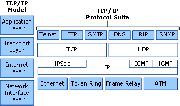
DNS is a hierarchical naming system used to map human-readable machine names into Internet Protocol addresses (IP addresses) for the Internet.[1] Although IP addresses provide a compact representation for identifying machines, users prefer to assign machines with pronounceable, meaningful, and easy-to-remember names.[1] DNS can be thought of as the Internet’s Phone Book. Instead of looking up a phone number using the person’s name or business’s name, the IP address can be looked up by using the domain name. For example, DNS translates the domain name www.mcmaster.ca into 130.113.64.65. DNS is also able to translate from IP addresses to domain names, which is known as Reverse Mapping or Inverse Mapping.[1]DNS is part of the Application Layer of the TCP/IP Internet Protocol Suite. It has two conceptually independent aspects. It specifies the name syntax and rules for delegating authority over names as well as the implementation of a system that efficiently maps names to addresses.[1]
Contents |
History of DNS
DNS[1]
Name Syntax And Rules Of DNS
Delegation Of Authority For Names
Subset Authority
Top-Level Domains
Name Syntax And Type
Implementation of DNS
Mapping Domain Names To Addresses
Domain Name Resolution
Caching
Domain Name System Message Format
Abbreviation Of Domain Names
Security Concerns
Domain Registration
References
- Comer, D. E. (2006). The domain name system (DNS). Internetworking with TCP/IP (Fifth ed., pp. 419-441). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- "What is DNS?: Domain Name System(DNS)". Retrieved on 2009-04-07
- "History of the Domain Name System". Retrieved on 2009-04-07.
- "History of Domain Name System". Retrieved on 2009-04-07.
See Also
External Links
--Jacky Ng (Ngck) 00:27, 8 April 2009 (EDT)