Peer To Peer Network Security
From Computing and Software Wiki
Peer-to-Peer (or P2P) networking is a fairly popular networking concept. Networks such as BitTorrent and eMule make it easy for people to find what they want and share what they have. P2P networks are used primarily to exchange pirated audio, video, software, and other inappropriate content. [5, 6]
Contents |
What is Peer To Peer Network
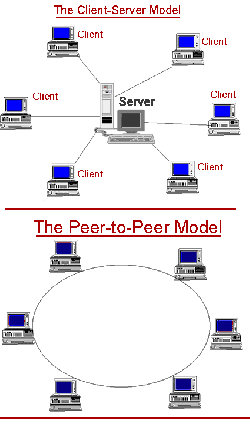
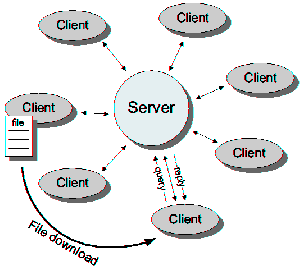
A pure peer-to-peer network does not have the notion of clients or servers, but only equal peer nodes that simultaneously function as both "clients" and "servers" to the other nodes on the network. A typical example for a non peer-to-peer file transfer is an FTP server where the client and server programs are quite distinct, and the clients initiate the download/uploads and the servers react to and satisfy these requests. [3]
Architecture
Unstructured P2P networks
Structured P2P networks
Security Problem
Applications
An important goal in peer-to-peer networks is that all clients provide resources, including bandwidth, storage space, and computing power. Thus, as nodes arrive and demand on the system increases, the total capacity of the system also increases. [3]
Peer-to-peer can be used for:
- File sharing
- Telephony
- Streaming media
- Software publication and distribution
References
- [1]http://www.spinellis.gr/pubs/jrnl/2004-ACMCS-p2p/html/AS04.html
- [2]http://www.ibiblio.org/team/intro/search/search.html
- [3]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peer-to-peer
- [4]http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/java/library/j-p2ptrust/
- [5]http://netsecurity.about.com/od/newsandeditorial1/a/p2psecurity.htm
- [6]http://www.websense.com/global/en/ResourceCenter/p2p_security.php
See Also
External Links
--Chowkw 00:12, 5 April 2008 (EDT)