Bluetooth
From Computing and Software Wiki
The Bluetooth was developed in 1994 by Sven Mattisson and Jaap Haartsen, working for Ericsson Mobile Platforms in Lund, Sweden.
Bluetooth was named after a late tenth century king, Harald Bluetooth, King of Denmark and Norway. He is known for his unification of previously warring tribes from Denmark (including Scania, present-day Sweden) and Norway. Bluetooth likewise was intended to unify different technologies, such as computers and mobile phones.
Bluetooth offers services that enable the connection of devices and the exchange of a variety of data classes between these devices. Bluetooth wireless technology is a short-range communications system mean to substitute the wires connecting electronic devices. It is a standard that wirelessly connects mobile phones, portable computers, cars, stereo headsets, MP3 players, and more. The key features of Bluetooth wireless technology are robustness, low power, and low cost. The specifications were formalized on May 20, 1998, by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG).
Contents |
The Technology
Band of Emission
The Bluetooth RF (Radio Frequency) operates in the unlicensed ISM 5Industrial, Scientific and Medical) band at 2.4GHz to 2.485GHz using 79 channels at 1MHz intervals to give a good interference immunity. The system utilizes a frequency hop transceiver, full-duplex signal at a nominal rate of 1600 hops/sec, to reduce interferences, and provides many FHSS (Frequency Hop Spread Spectrum) carriers. By detecting and avoiding the frequencies the others devices are using, the AFH (Adaptive Frequency Hoping) runs through the available frequency. This adaptive hopping allows for more efficient transmission within the spectrum, providing users with greater performance even if using other technologies along with Bluetooth technology
Range
The operating range depends on the device class:
- Class 1 radios:
- Used primarily in industrial use cases
- Have a range of 100 meters or 300 feet
- Maximum Permitted Power: 100mW/20dBm
- Class 2 radios:
- Most commonly found in mobile devices
- Have a range of 10 meters or 33 feet
- Maximum Permitted Power: 2.5mW/4dBm
- Class 3 radios:
- Have a range of up to 1 meter or 3 feet
- Maximum Permitted Power: 1mW/0dBm
Bluetooth Baseband - Networking
Bluetooth communication occurs between a master radio and a slave radio. Bluetooth radios are symmetric in that the same device may operate as a master and also the slave. Each radio has a 48-bit unique device address that is fixed.
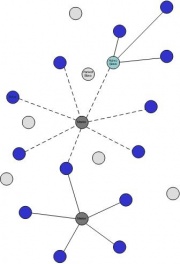
Piconet
When two Bluetooth devices are linked, a piconet is created.A piconet is a mini network, composed by two or more devices, and has a star topology. The devices occupy the same physical channel, hence they are synchronized to a common clock and hopping sequence. The common clock is the clock of one of the device, named the master and the hopping sequence depends on the master’s clock and the master’s device address. The other devices are named slaves. Within a common location a number of independent piconets may exist. Each piconet has a different physical channel that is a different master device and an independent piconet clock and hopping sequence. Bluetooth technology protocols allow one master device to interconnect with up to seven active devices. Up to 255 further devices can be inactive, or parked, which the master device can bring into active status at any time. At any given time, data can be transferred between the master and one other device. However, the master switches rapidly from device to another in a round-robin fashion. (Simultaneous transmission from the master to multiple other devices is possible, but not used much.) Either device can switch roles and become the master at any time.
Scatternet
A Bluetooth enabled device may participate concurrently in two or more piconets. It does this on a time-division multiplexing basis. Since the piconet is defined by synchronization to the master’s Bluetooth clock a Bluetooth enabled device can never be a master of more than one piconet. However, it may be a slave in many independent piconets. There may be a maximum of 10 fully loaded piconets in a scatternet. Each node can serve both as a host and as a router. Thus, any device in a piconet can connect to a device in an adjacent piconet.
--Morsall 15:18, 12 April 2009 (EDT)