Network-Based Software Architectures
From Computing and Software Wiki
Network-Based Software Architecture is a subfield of the area of Software Architectures that deals with the conceptual structure of a software system that primarily runs on a network, e.g. Apache Web Server.
Contents |
History and Introduction
As software increased in size, interaction, and sophistication, the need for a conceptual or a birds-eye-view of a software system became a central issue in software engineering research in the early 90s [4]. While the field has not reached the level of maturity that building architecture, for example, enjoys, it has started finding its way into mainstream software development, and "software architects" have become an important commodity for most software projects.
As the World Wide Web continues to infiltrate our every day life, our level of reliance on software keeps increasing significantly . This gave rise to a new specialty of software architecture; architecture of network-based software, initially introduced in Roy Fielding's PhD dissertation [2].
Classification
Software architectures have been categorized by observation. Seeing how successful software evolves, researchers were able to devise a number of categories that generally describe the most ubiquitous architectures, usually called "accidental" architectures. The name "accidental architectures" has been given since the the organization of these software systems did not follow any engineering guidelines and evolved with time until they took a permanent shape. [1], [3]
The following sections explain and illustrate some categories of network-based software architectures.
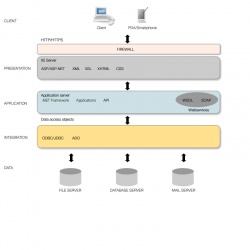
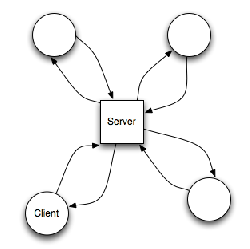
Client-Server
One of the most widespread styles in network-based applications. Consists of client based software and server based software where the server serves a number of clients concurrently. The client software is separated from the server software and the mode of communication between is defined.
Code On Demand (COD)
In COD, the clients request the code from the server as they need it. The code is received and is executed on the client's machine. This reduces the load on the server and gives a higher quality of service to the client. [2]
References
[1] Bass, Clements & Kazman, Software Architecture in Practice, Addison-Wesley 1998
[2] Fielding, Roy Thomas. Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-based Software Architectures. Doctoral dissertation, University of California, Irvine, 2000.
[3] Grady Booch. The Architecture of Web Applications. IBM Developer Works. 01 Jun 2001. IBM. Last Accessed on 13 March 2008. <http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/ibm/library/it-booch_web/>.
[4] D. Garlan and M. Shaw. An Introduction to software architecture. In Advances in Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering, pages 1-39, Singapore, 1993. World Scientific Publishing Company.
See also
External links
- Worldwide Institute of Software Architecture (WWISA)
- Software Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon: Software Architecture Group
- Roy Fielding's homepage
- Grady Booch's Software Architecture Blog
--65.92.69.11 21:38, 2 April 2008 (EDT)