Piggybacking
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Statistics == | == Statistics == | ||
=== Online Poll === | === Online Poll === | ||
| - | + | [[Image:Online_poll.jpg|right|thumb|This poll has over 3000 votes]] | |
From an online poll taken from lifehacker.com since March 2006, just a little above 60% of voters said they would gladly hop onto someone’s wireless network if they didn’t have access to their own at the moment. | From an online poll taken from lifehacker.com since March 2006, just a little above 60% of voters said they would gladly hop onto someone’s wireless network if they didn’t have access to their own at the moment. | ||
A little below 25% of voters said they piggybacking is their main source of internet. | A little below 25% of voters said they piggybacking is their main source of internet. | ||
Combined that’s 85% of voters admitting to the practice. | Combined that’s 85% of voters admitting to the practice. | ||
About 7% said they sometimes piggyback but only in an emergency while 8% said their morals would never allow them to do such a thing. | About 7% said they sometimes piggyback but only in an emergency while 8% said their morals would never allow them to do such a thing. | ||
| - | + | <br style="clear:both;"/> | |
=== McMaster University Poll === | === McMaster University Poll === | ||
| - | + | [[Image:Mcmaster_poll.jpg|left|thumb|This poll had 100 votes]] | |
Just as a comparison, I conducted a small survey sampling our fellow students at McMaster. I attempted to cover a broad range of students from different faculties so I only asked a few students in this class as I did not want to contaminate the data with biased answers. About 55% of the students I surveyed admitted to have piggybacked before and 45% said they have not. Mind you, I was patiently waiting for them to finish filling out the survey so I suspect some may have not been telling the truth in fear of embarrassment. | Just as a comparison, I conducted a small survey sampling our fellow students at McMaster. I attempted to cover a broad range of students from different faculties so I only asked a few students in this class as I did not want to contaminate the data with biased answers. About 55% of the students I surveyed admitted to have piggybacked before and 45% said they have not. Mind you, I was patiently waiting for them to finish filling out the survey so I suspect some may have not been telling the truth in fear of embarrassment. | ||
Of all the student’s surveyed, only about 20% expressed concerned about security issues when using somebody’s wireless network and said they would not send passwords or do any other information sensitive actions. | Of all the student’s surveyed, only about 20% expressed concerned about security issues when using somebody’s wireless network and said they would not send passwords or do any other information sensitive actions. | ||
| - | + | <br style="clear:both;"/> | |
== Views and Ethics == | == Views and Ethics == | ||
Advocates for piggybacking state that the practice is harmless and compare it to drinking from a public water fountain or sharing a cup of sugar. One writes, “Leaving a network open is just being a good neighbor”. | Advocates for piggybacking state that the practice is harmless and compare it to drinking from a public water fountain or sharing a cup of sugar. One writes, “Leaving a network open is just being a good neighbor”. | ||
Revision as of 07:35, 1 December 2007
Piggybacking internet access is the practice of gaining network services of someone’s wireless connection without the owner’s explicit permission or knowledge by moving their own computer into range of the broadcasting access point in question.
Contents |
Background
The recent explosive growth of wireless technology found in the market can be attributed to the many benefits wireless telecommunications provide. From the casual Internet surfer to the technological inclined power user, wireless networks provide the convenience of mobility, keeping up with today’s trends in increasing portability and decreasing size of our devices. Unfortunately, wireless networks also suffer from more attacks and abuse because of how easy it is to locate and connect to wireless networks in comparison to traditional wired ones. In combination with the lack of strong default security counter measures, the controversial practice of piggybacking has increasingly become more common.
Piggybacking should not be confused with wardriving which involves only the mapping of the insecure access points. In addition, people connecting to a hotspot service provided by businesses is generally not considered as piggybacking.
Statistics
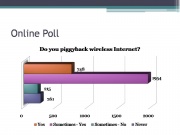
Online Poll
From an online poll taken from lifehacker.com since March 2006, just a little above 60% of voters said they would gladly hop onto someone’s wireless network if they didn’t have access to their own at the moment.
A little below 25% of voters said they piggybacking is their main source of internet.
Combined that’s 85% of voters admitting to the practice.
About 7% said they sometimes piggyback but only in an emergency while 8% said their morals would never allow them to do such a thing.
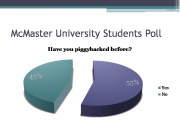
McMaster University Poll
Just as a comparison, I conducted a small survey sampling our fellow students at McMaster. I attempted to cover a broad range of students from different faculties so I only asked a few students in this class as I did not want to contaminate the data with biased answers. About 55% of the students I surveyed admitted to have piggybacked before and 45% said they have not. Mind you, I was patiently waiting for them to finish filling out the survey so I suspect some may have not been telling the truth in fear of embarrassment.
Of all the student’s surveyed, only about 20% expressed concerned about security issues when using somebody’s wireless network and said they would not send passwords or do any other information sensitive actions.
Views and Ethics
Advocates for piggybacking state that the practice is harmless and compare it to drinking from a public water fountain or sharing a cup of sugar. One writes, “Leaving a network open is just being a good neighbor”. Advocates against piggybacking compare the practice to entering a home just because it is unlocked or stealing cable from your neighbor with a splitter.
Besides the bandwidth loss, a person can commit some serious crimes with the Internet services he or she gains through piggybacking, such as hacking into sensitive information, downloading child pornography, etc.
Prevention
There are several ways to prevent piggybacking however some are more effective than others.
WEP
It is very ineffective against people with a little computer knowledge and the will to gain access to the network since WEP is cryptographically weak and takes only a few minutes to crack. There have been attempts to enhance the security such as:
- WEP2
- WEP+
- dynamic WEP which changes the key periodically
None are substantially more effective.
MAC Address Authentication
A computer trying to connect to the network will be allowed to do so if and only if their MAC address conforms the list of allowed MAC addresses. This is cumbersome to setup for the administrator as he or she will have to add everyone’s MAC address to the list. This method does not prevent data from being stolen since there is no encryption. And even then, an attacker can observe network traffic and obtain valid MAC addresses and then spoof their MAC address to gain access.
IPSec
Ip security or IPSec is used to encrypt traffic, reducing or possibly eliminating all plain text information sent across the network. It is composed of a suite of protocols such as authentication, encrypting IP packets, or cryptographic key establishment as we have read about in Chapter 9 Key Management of the textbook.
WPA
Wi-FI protected access, commonly referred to as WPA, was created by Wi-Fi Alliance and one of the major improvements over WEP is the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol which basically changes the key dynamically as the system is being used. WPA also boasts a more secure message integrity code or MIC with the Michael algorithm. Later, they introduced WPA2 which strengthens the security with new algorithms such as CCMP which stands for Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Protocol.
Legalities
Canada
While there are many differences in the laws between one country and another, in Canada the law could be interpreted in such a way that makes piggybacking illegal. A Toronto lawyer Gil Zvulony commented on CBC’s Spark Radio recently and says that if the police ever showed up because you were piggybacking, the only way you can be charged was if the crown could proof you knew that you were doing something wrong.
The closest thing someone being charged with piggybacking was where a Toronto man was caught literally with his pants down downloading child pornography using someone's wireless network. Ultimately, he was charged for the pornography and not the piggybacking.
Singapore
In Singapore, Garyl Tan Jia Luo became the first man to be convicted of piggybacking on January 16th, 2007 and was sentenced for 18 months probation with 80 hours of community service.