Corporate Security and IT Policies
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
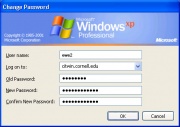
[[Image:Passwordchange.jpg|thumb|A user password policy change window shown in Windows XP.[X]]] | [[Image:Passwordchange.jpg|thumb|A user password policy change window shown in Windows XP.[X]]] | ||
| - | + | In some organizations, users do not have rights to install or modify major components of the operating system. This is to prevent opening ports, and installing software which could be open to malicious attack. Software updates are also typically enforced, to keep computers up-to-date with the latest software - decreasing the risk of known attacks. | |
From a software perspective, corporations protect local data with encryption and backup, intruders from outside the organization with firewalls, as well as internal threats | From a software perspective, corporations protect local data with encryption and backup, intruders from outside the organization with firewalls, as well as internal threats | ||
Revision as of 02:00, 13 April 2009
Corporations need to protect their physical and soft assets in today’s world of thieves and hackers. To do so, they implement IT and Security Policies, which protect their corporations against such attacks. These prevention mechanisms can be split up into three main categories: physical, software, and social (employees). The ultimate goal is to convince a potential attacker that sufficient security measures are in place such that the attack will not be worth while.[X]
Contents |
Physical Security
Tech-savvy companies rarely forget software security, or the importance of it. However, physical security is sometimes lowered in priority, given the movement towards a paperless work environment. Physical security is an important security layer, because a decreased guard in this layer could allow for easier software attacks. This could allow physical access to internal computers and therefore increasing probability of software attacks from computers within the organization, which is considered very dangerous.
Security Cards (or access badges) are a common security feature, typically used on all entrances to secured buildings. Usually a public lobby-area with a receptionist is open for visitors, however, access to the remaining parts of the building are secured with a locked system which requires authorized employees to swipe security passes to gain access.
Miniature mirrors can be used on monitors to allow workers using a computer screen to see what’s behind them. The main purpose of these mirrors is to allow the user to see when unwanted eyes from behind are trying to view confidential information on their screen.
Other relatively self-explanatory physical security features include:
- Door locks - lock offices and rooms of higher importance such as the server room
- Cabinet Locks - safe-keep confidential documents
- Security Cameras - monitor internal and external activities; typically recorded and monitored 24 hours a day
- Shredders - shredding machines are frequently located in offices to prevent dumpster diving; a service is sometimes used from a company that performs paper shredding for a fee.
If these security measures are breached, and an attack does take place, a good security measure to have is an intrusion detection system. A safe system would consist of an alarm, combined with an automated notification system. [X]
Software Security
Software security refers to the protection of digital data; this topic also includes hardware necessary to implement software security, such as a computer running the corporate firewall.
Security from a software perspective is typically handled by a designated team of network administrator or security administrators. They are responsible for setting the IT Policies that govern employees of the corporation such that all corporate computer systems are safe from attacks.
A typical security practice is to enforce users to change their passwords at a standard interval - such as every 2 months. Furthermore, a password policy is complementary and can enforce users to create passwords consisting of:
- A minimum number of characters
- A minimum number of letters
- A minimum number of numbers
- A minimum number of upper case characters
- A minimum number of non-alphanumeric symbols
In some organizations, users do not have rights to install or modify major components of the operating system. This is to prevent opening ports, and installing software which could be open to malicious attack. Software updates are also typically enforced, to keep computers up-to-date with the latest software - decreasing the risk of known attacks.
From a software perspective, corporations protect local data with encryption and backup, intruders from outside the organization with firewalls, as well as internal threats
Social Employee Security
Although smaller companies sometimes omit discussion social engineering within their security practices, it is strikingly one of the most important areas to cover. Essentially, this type of security mechanism aims to prevent social engineering.
Companies typically have a statement in their security policy manual such as [X]:
Don't reveal a password to the boss
Don't talk about a password in front of others
Don't hint at the format of a password (e.g., "my family name")
Don't reveal a password over the phone to ANYONE
Don't reveal a password to co-workers while on vacation
If someone demands a password, refer them to this document or have them call someone in the Information Security Department.
IT Administrators typically do not have direct access to view account passwords. Instead, passwords are typically encrypted, and should a user forget his or her password, the administrator must reset the password, rather than being able to view the user’s former password and give it out.
People Security – IT Desk taught against social networking, never give out passwords over phone, only email (which is secured with password)
Other Security measures
People Security – IT Desk taught against social networking, never give out passwords over phone, only email (which is secured with password)
Password Standard (#characters, variety of characters, password chaged every 2 months) Secure communications (128 triple A or something, blackberry encrypted)
References
Some companies have statements of security as shown here: http://www.total.com/static/en/medias/topic1608/pol-sur-001_security_policy12.pdf
picture: http://www.rsscctv.com/images/P/200x200_tkc215_300%2520WEB.jpg
password change policy: http://support.netmail.sg/images/changepwd_owa2.gif
password Policy: http://www.sans.org/resources/policies/Password_Policy.pdf
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physical_Security
password change pic: http://www2.cit.cornell.edu/services/systems_support/images/changepassword2.jpg
Mirror monitor picture: http://www.grand-illusions.com/acatalog/monitor_mirror.jpg