ZigBee
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| - | ZigBee is defined and promoted by the ZigBee Alliance, a group of over 150 companies. The current push is for industrial plants where low cost and long battery life remote sensors are required for process control and preventative machine maintenance. | + | ZigBee is defined and promoted by the ZigBee Alliance, a group of over 150 companies. The latest version of the ZigBee specification is ZigBee-2007. The current push is for industrial plants where low cost and long battery life remote sensors are required for process control and preventative machine maintenance. |
== Uses == | == Uses == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
ZigBee is based on radio frequency (RF) technology and mesh networking. | ZigBee is based on radio frequency (RF) technology and mesh networking. | ||
| - | It is a suite of protocols that covers from the | + | It is a suite of protocols that covers from the physical layer, network layer to the application layer. The physical layer is an implementation of IEEE 802.15.4 (Bluetooth is covered under IEEE 802.15.1). |
=== Standards === | === Standards === | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
<br>Zigbee is designed to operate near other wireless standards. [2]]] | <br>Zigbee is designed to operate near other wireless standards. [2]]] | ||
| - | ZigBee | + | ZigBee implements the IEEE 802.15.4 WPAN standard, which specifies the media-access control (MAC) and physical-layer. This ensures interoperability with other stand-compliant products. This standard specifies operation in the unlicensed bands: |
* 2.4 GHz for global use | * 2.4 GHz for global use | ||
* 915 MHz for N. America, Australia, and a few other counties | * 915 MHz for N. America, Australia, and a few other counties | ||
* 868 MHz for EU countries [2] | * 868 MHz for EU countries [2] | ||
| - | ZigBee specification is defined and promoted by ZigBee Alliance. The alliance is an independent, vendor-neutral and non-profit corporation founded in 2002. [2] Adopters of ZigBee technology must licence the technology by becoming members of the alliance. Manufactures must apply for ZigBee certification, which is meant satisfy | + | ZigBee specification is defined and promoted by ZigBee Alliance. The alliance is an independent, vendor-neutral and non-profit corporation founded in 2002. [2] Adopters of ZigBee technology must licence the technology by becoming members of the alliance. Manufactures must apply for ZigBee certification, which is meant to satisfy the minimum conformance to ZigBee standard. This in indented to promote device interoperability, and reputation of ZigBee standard. |
The actual specification is available for non-profit use. The brief history of the specification is: | The actual specification is available for non-profit use. The brief history of the specification is: | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
ZigBee standard provides network and application layer. The network layer deals with security management, message broker, routing information and general network management. The security is done at both network and application level, using AES-128 symmetric keys for authentication and encryption. [2] Since it is defined in the specification, all ZigBee products will provide as minimum, which allows for a very secure environment. Developers can provide more security features at the application level. | ZigBee standard provides network and application layer. The network layer deals with security management, message broker, routing information and general network management. The security is done at both network and application level, using AES-128 symmetric keys for authentication and encryption. [2] Since it is defined in the specification, all ZigBee products will provide as minimum, which allows for a very secure environment. Developers can provide more security features at the application level. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ZigBee's interface to the end-use is at the Application layer. In order to facilitate interoperabilty between devices that accoplish a specific task, ZigBee standard has defined Application Profiles [1], similar to Bluetooth Profiles. Application Profile is an agreement on a series of messages defining an application space. For example, ''Home Automation'' profile allows a light sensor product from one vendor to work with light controller product from another vendor. [2] ZigBee offer two types of Application Profiles: | ||
| + | # Public Application Profiles | ||
| + | These are defined by ZigBee Standard and intended for consumer's information purpose. Currently, only ''Home Automation'' profile is defined. Some other profiles in development are ''Telecommunication Services'', and ''Personal Home Healthcare''[2]. | ||
| + | # Manufacturing Specific Profiles | ||
| + | These are private application profiles developed for a company. These may be proprietary, often intended for plant use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Developers develop at the Application level. There are two levels o | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Topology === | ||
Revision as of 00:19, 14 April 2008
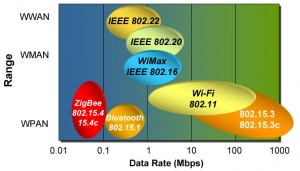
ZigBee, is a wireless open standard and a competing protocol to Bluetooth, which fall under wireless personal area network (WPAN) classification. It is a standard for mesh networking, with allows for self configuring networks, ease of installation and configuration. It is designed for low power applications, especially applications that are designed for very long batter life. It has a low data rate of 20-250Kbps, depending on the band. The protocol is designed with security in mind.
ZigBee is defined and promoted by the ZigBee Alliance, a group of over 150 companies. The latest version of the ZigBee specification is ZigBee-2007. The current push is for industrial plants where low cost and long battery life remote sensors are required for process control and preventative machine maintenance.
Contents |
Uses
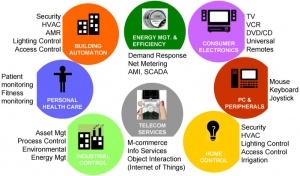
It is intended to be used for home entertainment and monitoring sensors, mobile services such as m-payment and m-healthcare, commercial building monitoring such as HVAC and access control. For manufacturing the current application is for low power, low data rate wireless sensor networks (WSN).
Technical Information
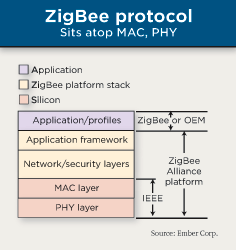
ZigBee is based on radio frequency (RF) technology and mesh networking. It is a suite of protocols that covers from the physical layer, network layer to the application layer. The physical layer is an implementation of IEEE 802.15.4 (Bluetooth is covered under IEEE 802.15.1).
Standards
ZigBee implements the IEEE 802.15.4 WPAN standard, which specifies the media-access control (MAC) and physical-layer. This ensures interoperability with other stand-compliant products. This standard specifies operation in the unlicensed bands:
- 2.4 GHz for global use
- 915 MHz for N. America, Australia, and a few other counties
- 868 MHz for EU countries [2]
ZigBee specification is defined and promoted by ZigBee Alliance. The alliance is an independent, vendor-neutral and non-profit corporation founded in 2002. [2] Adopters of ZigBee technology must licence the technology by becoming members of the alliance. Manufactures must apply for ZigBee certification, which is meant to satisfy the minimum conformance to ZigBee standard. This in indented to promote device interoperability, and reputation of ZigBee standard.
The actual specification is available for non-profit use. The brief history of the specification is:
- The ZigBee specifications were ratified on 14 December 2004.
- The ZigBee Alliance announces public availability of Specification 1.0 on 13 June 2005, known as ZigBee 2004 Specification.
- The ZigBee Alliance announces the completion and immediate member availability of the enhanced version of the ZigBee Standard in September 2006, known as ZigBee 2006 Specification.
- During the last quarter of 2007, ZigBee PRO, the enhanced ZigBee specification was finalized. [7]
Protocol
ZigBee standard provides network and application layer. The network layer deals with security management, message broker, routing information and general network management. The security is done at both network and application level, using AES-128 symmetric keys for authentication and encryption. [2] Since it is defined in the specification, all ZigBee products will provide as minimum, which allows for a very secure environment. Developers can provide more security features at the application level.
ZigBee's interface to the end-use is at the Application layer. In order to facilitate interoperabilty between devices that accoplish a specific task, ZigBee standard has defined Application Profiles [1], similar to Bluetooth Profiles. Application Profile is an agreement on a series of messages defining an application space. For example, Home Automation profile allows a light sensor product from one vendor to work with light controller product from another vendor. [2] ZigBee offer two types of Application Profiles:
- Public Application Profiles
These are defined by ZigBee Standard and intended for consumer's information purpose. Currently, only Home Automation profile is defined. Some other profiles in development are Telecommunication Services, and Personal Home Healthcare[2].
- Manufacturing Specific Profiles
These are private application profiles developed for a company. These may be proprietary, often intended for plant use.
Developers develop at the Application level. There are two levels o
Topology
Interoperability
Zigbee is designed to operate near other devices. ZigBee falls within the 802 family of standards, which includes Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
There has been some speculation that use of 2.4Ghz bandwidth introduces significant interferance. Such claims have been refuted by a paper released by ZigBee alliance.[6]
Market
With the WSN market grow to estimated $4.6 billion in 2011, up from $500 million in 2007; ZigBee is a strong contender to become the standard for WSN. Companies can adopt this protocol into its products in an attempt to gain the market share. Also, industrials plants can gain the benefits from better monitoring and control of process, thanks to the lost cost and easy of deployment of wireless sensor networks based on ZigBee.
See also
References
- ZigBee Overview. Retrieved on April 5, 2008 from <[1]>
- An Overview of ZigBee - The Power of the Mesh. Retrieved on April 5, 2008 from <[2]>
- Home networking with Zigbee. Retrieved on April 3, 2008 from <[3]>
- Choosing wisely for embedded ZigBee apps. Retrieved on April 3, 2008 from <[4]>
- ZigBee specification. Retrieved on April 3, 2008 from <[5]>
- ZigBee and Wireless Frequency Coexistence. Retrieved on April 5, 2008 from <[6]>
External links
- Test