Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) Protocol
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | The Secure Eletronic Transaction (SET) Protocol was created by the the credit cards companies VISA and MasterCard. It`s main objective is to secure transactions with credit cards over insecure networks. The SET protocol relies on cryptography and [[Digital Cerificate]] to ensure the authenticity of the users, confidentially of information and the payment`s integrity. | + | The Secure Eletronic Transaction (SET) Protocol was created by the the credit cards companies VISA and MasterCard (involving other companies such as GTE, IBM, Microsoft, Netscape, RSA and VeriSign) starting in 1996. It`s main objective is to secure transactions with credit cards over insecure networks. The SET protocol relies on [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cryptography cryptography] and [[Digital Cerificate]] to ensure the authenticity of the users, confidentially of information and the payment`s integrity. |
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Dual Signature == | == Dual Signature == | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | The data of a payment on a trasaction made by a customer includes information that concearn only to the merchant (Order Information) and only to the bank (Payment Information), that means, two messages for two different destinations. The Dual Signature permits that those information to be sent in single transaction protected by | |
| + | [http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Digital_Signatures Digital Signature]. By doing this, the information will be delivered only to right destination, providing to the customers more privacy. This "linked" information also permits disputes between the involved parts(like miss calculations, erroneous charges or to determine if a payment that belongs to a specifc order) to be solved more easily. | ||
| - | + | === Operation === | |
| + | This dual Signature works by encrypting the order information with the merchant`s public key an the information that refers to the payment is encrypted with the bank`s public key. The informations from the payment and from the order are hashed and the result is concatenated. Then the concatenated result is again hashed then encrypted with the customer`s key, generating the dual signature. | ||
| + | <math>Dual Signature = EKRC { H [ H(PI) || H(OI) ] }</math> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
where EKRC -> customer private key | where EKRC -> customer private key | ||
| Line 82: | Line 64: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| - | [http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~jervis/cs3235/set.html] | + | [http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~jervis/cs3235/set.html Data Security for e-Transaction] |
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.samconline.com/samc/6340/Chapter-11-e-commerce/sld014.htm SET Electronic Transmission Protocol] | ||
| - | [http:// | + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secure_electronic_transaction Secure Electronic Transaction] |
| + | [http://www.davidreilly.com/topics/electronic_commerce/essays/secure_electronic_transactions.html Secure Electronic Transactions] | ||
| - | + | --[[User:Nobrem|Nobrem]] 21:30, 13 April 2008 (EDT) | |
| - | --[[User:Nobrem|Nobrem]] | + | |
Revision as of 01:30, 14 April 2008
The Secure Eletronic Transaction (SET) Protocol was created by the the credit cards companies VISA and MasterCard (involving other companies such as GTE, IBM, Microsoft, Netscape, RSA and VeriSign) starting in 1996. It`s main objective is to secure transactions with credit cards over insecure networks. The SET protocol relies on cryptography and Digital Cerificate to ensure the authenticity of the users, confidentially of information and the payment`s integrity.
Contents |
Overview
All users of SET must first be registered with the Certificate Authority before a transaction is allowed to take place. Digital Certificate is used to ensure confidentially of any transactions. If a transaction is needed, both parties will then exchange their certificate.
The sender will use the randomly generated session key to encrypt all the messages and use the recipient's public key to encrypt the session key. This is known as "digital envelop" of the message.
The recipient will then decrypt the digital envelop using his private key and uses the symmetric key to obtain the original message.
SET uses both the secret key (impractical as each customer need a distinct key) and public key cryptography (merchant would only need to publish his public key and the customer would be able to send a secure message to him.)
Dual Signature
The data of a payment on a trasaction made by a customer includes information that concearn only to the merchant (Order Information) and only to the bank (Payment Information), that means, two messages for two different destinations. The Dual Signature permits that those information to be sent in single transaction protected by Digital Signature. By doing this, the information will be delivered only to right destination, providing to the customers more privacy. This "linked" information also permits disputes between the involved parts(like miss calculations, erroneous charges or to determine if a payment that belongs to a specifc order) to be solved more easily.
Operation
This dual Signature works by encrypting the order information with the merchant`s public key an the information that refers to the payment is encrypted with the bank`s public key. The informations from the payment and from the order are hashed and the result is concatenated. Then the concatenated result is again hashed then encrypted with the customer`s key, generating the dual signature. <math>Dual Signature = EKRC { H [ H(PI) || H(OI) ] }</math>
where EKRC -> customer private key
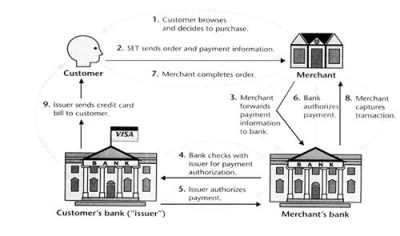
General Steps
Customer to Merchant
Customer sends both the order and payment details to the merchant, together with his certificate.
The payment details will be encrypted; merchant will not be able to read the payment details.
The merchant uses the customer certificate to verify the customer.
Merchant to Customer's Bank
Merchant will send this payment details to his bank who will then forward it to the customer's bank to request authorization that the customer has sufficient available credit for the purchase.
Confirmation of Order
Once the authorization is received, the merchant will send an order confirmation to the customer.
Shipping of Goods
Upon confirmation by the customer, the merchant will deliver the goods to the customer
Request for Payment By Merchant
Lastly, the bank makes a request to the customer's credit card bank for payment.
References
- Data Security for e-Transaction. Retrieved on April 12th 2008, from <http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~jervis/cs3235/set.html>
- SET Electronic Transmission Protocol. Retrieved on April 12th 2008, from <http://www.samconline.com/samc/6340/Chapter-11-e-commerce/sld014.htm>
External links
Data Security for e-Transaction
SET Electronic Transmission Protocol
Secure Electronic Transactions
--Nobrem 21:30, 13 April 2008 (EDT)