Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) Protocol
From Computing and Software Wiki
(New page: The Secure Eletronic Transaction (SET) Protocol was created by the the credit cards companies VISA and MasterCard. It`s main objective is to secure transactions with credit cards over inse...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The Secure Eletronic Transaction (SET) Protocol was created by the the credit cards companies VISA and MasterCard. It`s main objective is to secure transactions with credit cards over insecure networks. The SET protocol relies on cryptography and [[Digital Cerificate]] to ensure the authenticity of the users, confidentially of information and the payment`s integrity. | The Secure Eletronic Transaction (SET) Protocol was created by the the credit cards companies VISA and MasterCard. It`s main objective is to secure transactions with credit cards over insecure networks. The SET protocol relies on cryptography and [[Digital Cerificate]] to ensure the authenticity of the users, confidentially of information and the payment`s integrity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Overview == | ||
| + | |||
| + | All users of SET must first be registered with the Certificate Authority before a transaction is allowed to take place. Digital Certificate is used to ensure confidentially of any transactions. If a transaction is needed, both parties will then exchange their certificate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The sender will use the randomly generated session key to encrypt all the messages and use the recipient's public key to encrypt the session key. This is known as "digital envelop" of the message. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The recipient will then decrypt the digital envelop using his private key and uses the symmetric key to obtain the original message. | ||
| + | |||
| + | SET uses both the secret key (impractical as each customer need a distinct key) and public key cryptography (merchant would only need to publish his public key and the customer would be able to send a secure message to him.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Dual Signature == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Benefits of Dual Signature | ||
| + | |||
| + | Information will only be released on a “Need-to-know” basis. Therefore, the merchant will not need the customer's credit card details, and the bank do not need the details of the customer order. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In separating the information, customers will have an extra level of privacy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The separated information can also be easily linked together to resolve disputes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Why is this link so important?? | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the event of a dispute, this link is important as it is used to prove that a particular payment is meant for a particular order. | ||
| + | |||
| + | How does Dual Signature Work | ||
| + | |||
| + | The order information intended for the merchant is encrypted with merchant public key. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The payment information intended for the bank is encrypted with the bank public key. | ||
| + | |||
| + | How to create the dual signatures | ||
| + | |||
| + | The hash values of the payment and order information are concatenated (H (PI) || H (OI) and the result hashed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Customer will encrypt the fianl result with his private key, creating the dual signature. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Dual Signature = EKRC { H [ H(PI) || H(OI) ] } | ||
| + | |||
| + | where EKRC -> customer private key | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == General Steps == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Customer to Merchant === | ||
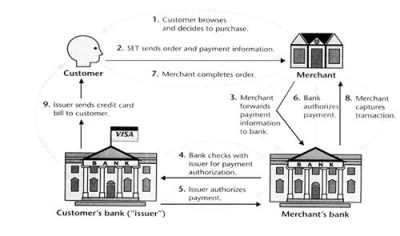
| + | [[Image:wikiimage1.jpeg |thumb|400px|right| '''General Steps''']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Customer sends both the order and payment details to the merchant, together with his certificate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The payment details will be encrypted; merchant will not be able to read the payment details. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The merchant uses the customer certificate to verify the customer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Merchant to Customer's Bank === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Merchant will send this payment details to his bank who will then forward it to the customer's bank to request authorization that the customer has sufficient available credit for the purchase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Confirmation of Order === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once the authorization is received, the merchant will send an order confirmation to the customer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Shipping of Goods === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Upon confirmation by the customer, the merchant will deliver the goods to the customer | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Request for Payment By Merchant === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lastly, the bank makes a request to the customer's credit card bank for payment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | #Data Security for e-Transaction. Retrieved on April 12th 2008, from <http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~jervis/cs3235/set.html> | ||
| + | #SET Electronic Transmission Protocol. Retrieved on April 12th 2008, from <http://www.samconline.com/samc/6340/Chapter-11-e-commerce/sld014.htm> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == External links == | ||
| + | [http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~jervis/cs3235/set.html] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.samconline.com/samc/6340/Chapter-11-e-commerce/sld014.htm] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
--[[User:Nobrem|Nobrem]] 23:15, 29 March 2008 (EDT) | --[[User:Nobrem|Nobrem]] 23:15, 29 March 2008 (EDT) | ||
Revision as of 23:34, 13 April 2008
The Secure Eletronic Transaction (SET) Protocol was created by the the credit cards companies VISA and MasterCard. It`s main objective is to secure transactions with credit cards over insecure networks. The SET protocol relies on cryptography and Digital Cerificate to ensure the authenticity of the users, confidentially of information and the payment`s integrity.
Contents |
Overview
All users of SET must first be registered with the Certificate Authority before a transaction is allowed to take place. Digital Certificate is used to ensure confidentially of any transactions. If a transaction is needed, both parties will then exchange their certificate.
The sender will use the randomly generated session key to encrypt all the messages and use the recipient's public key to encrypt the session key. This is known as "digital envelop" of the message.
The recipient will then decrypt the digital envelop using his private key and uses the symmetric key to obtain the original message.
SET uses both the secret key (impractical as each customer need a distinct key) and public key cryptography (merchant would only need to publish his public key and the customer would be able to send a secure message to him.)
Dual Signature
Benefits of Dual Signature
Information will only be released on a “Need-to-know” basis. Therefore, the merchant will not need the customer's credit card details, and the bank do not need the details of the customer order.
In separating the information, customers will have an extra level of privacy.
The separated information can also be easily linked together to resolve disputes.
Why is this link so important??
In the event of a dispute, this link is important as it is used to prove that a particular payment is meant for a particular order.
How does Dual Signature Work
The order information intended for the merchant is encrypted with merchant public key.
The payment information intended for the bank is encrypted with the bank public key.
How to create the dual signatures
The hash values of the payment and order information are concatenated (H (PI) || H (OI) and the result hashed.
Customer will encrypt the fianl result with his private key, creating the dual signature.
Dual Signature = EKRC { H [ H(PI) || H(OI) ] }
where EKRC -> customer private key
General Steps
Customer to Merchant
Customer sends both the order and payment details to the merchant, together with his certificate.
The payment details will be encrypted; merchant will not be able to read the payment details.
The merchant uses the customer certificate to verify the customer.
Merchant to Customer's Bank
Merchant will send this payment details to his bank who will then forward it to the customer's bank to request authorization that the customer has sufficient available credit for the purchase.
Confirmation of Order
Once the authorization is received, the merchant will send an order confirmation to the customer.
Shipping of Goods
Upon confirmation by the customer, the merchant will deliver the goods to the customer
Request for Payment By Merchant
Lastly, the bank makes a request to the customer's credit card bank for payment.
References
- Data Security for e-Transaction. Retrieved on April 12th 2008, from <http://www.comp.nus.edu.sg/~jervis/cs3235/set.html>
- SET Electronic Transmission Protocol. Retrieved on April 12th 2008, from <http://www.samconline.com/samc/6340/Chapter-11-e-commerce/sld014.htm>
External links
--Nobrem 23:15, 29 March 2008 (EDT)