Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 219: | Line 219: | ||
== '''See Also''' == | == '''See Also''' == | ||
| - | + | ||
| Line 226: | Line 226: | ||
| - | --- | + | [http://imps.mcmaster.ca/courses/SE-4C03-09/project/wiki-pages.html Other Networks Topics] |
| + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RFID other RFID] | ||
--[[User:Alhadds|Alhadds]] 10:35, 10 April 2009 (EDT) | --[[User:Alhadds|Alhadds]] 10:35, 10 April 2009 (EDT) | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 11 April 2009
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is a method to identify object automatically, it relies on storing and distantly obtaining data back using RFID tags. By using this technique and without any human role, objects are being identified and their data are being analysed by special computer systems.1
RFID has received too much of exhilarating discussion; it took over 50 years to progress from susceptible to an average application that aid management of manufactured goods and materials, this technology create a more proficient and well-ordered tracing and product management.2
RFID tag is a microchip intended for wireless data transmission which can be directed to be assembled into a product, animal, or a person to identify those using Radio-waves.3
If applied correctly, RFID can have a major impression on retail functioning and supply chain management. Automation is a leading factor when it comes to developing supply chain management to be well-organized, cost-effective and less cost process. Identification happens to be the most crucial part of automation. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) will be a clear key for the future and may also replace manual solutions such as bar code systems. Besides that, it may also be useful for more diverse and new objects.
This page covers the types of RFID system and components in details, such as: reader, tag middleware, antenna. This page also includes the characteristics of each part of the system with character that can affect its function.
Contents |
Wireless Communication and the Air Interface
RFID systems can be classified based on backscattered coupling, inductive coupling, magnetic coupling or capacitive coupling. By those ways, tag and its reader can wirelessly communicate to each other. (Coupling)
Data modulation of the data is the best way to assure that data transfers in very efficient way via space that separates the tag and the reader, this is could be done by amplitude, frequency, or phase- shift keying.4 (Modulation)
Carrier Frequencies
Carrier waves hold the data between the tag and its reader and they determine the data transfer rates, and there is a proportional relationship between the carrier frequency and the data are being transferred.5
Range and Power Levels
The power available within the tag and the one available at the reader, besides the environmental conditions control the range and power level that RFID system can attain.6
Environmental conditions meant to be the obstructions that absorb some of these waves, so that they affect the strength and intensity of the field, and it is surely different in every kind of materials.
RFID System Components
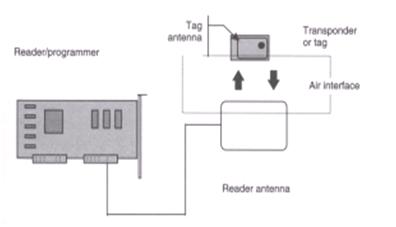
The necessary components that form an RFID system are tags and a reader (also called interrogator); an interrogator is created by combining a reader with a decoder and an interface (might be space or free air).Basic component of an RFID system is shown in the figure below.
Transponders and Tags
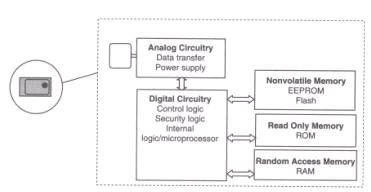
The phrase transponder comes from Transmitter and Responder, which explain the behaviour of the device. The tag reacts (responding) to a communicated (transmitting) demand for the data it controls. The space or air interface is the mean of communicating the reader with the tag wirelessly.Figure 2 shows a block diagram of a typical RFID transponder.7
Passive tag components
A passive tag contains three components that allow it to obtain and broadcast signals in a proficient way:
1- An integrated circuit or chip
- This chip’s purpose is to stock data and carry out specific orders and information. Generally the passive tags memory has range from 1 to 1000 bits. Read-only or read-write property can be determined by the chip’s design.
- Although tags are recognized by shape, but integrated circuit has more impact on overall tag performance. The chip is accountable for converting radio frequency energy into practical electrical power, storing and bringing back data, then modulating the backscatter. Silicon is the material that chip is made and that contributes to the cost of the tag.8
- There are some parameters that related to consumption and extraction, as well as the reflection of the power of RFID tag:
- Memory chip: the tag memory might consist of read-only memory ROM, random access memory RAM, and non-volatile programmable memory like EEPROM.
- The effectiveness in the circuit power while integrated chip converts the energy from tag’s antenna to specific tuned frequency.9
- Matching between the chip’s and antenna’s impedance: if not happening, the power will be reflected away and then it will not be useful to the tag.
- Capability of the chip to modify its antenna’s impedance: it can be done by backscatter method.
2- An antenna (or coupling element)
- The antenna’s purpose is to take radio frequency waves and distribute a signal back out. By using coupling process, the antenna collect energy form the radio frequency field, then powers the tag up and stimulate the chip, because the tag antenna must “couple” with the electromagnetic fields that the RFID reader has.
3- The substrate
- This is mostly made of plastic or Mylar to retain it all together and the antenna and the chip are attached to it.
Characteristics of RFID tags
Several characteristics sort RFID transponders out and form the core of device specifications, including:
- Operating frequency
- Four frequency ranges are generally distinguished for RFID systems: Low, High, and ultra high frequency, as well as microwave. As we go from low to microwave frequencies, the range can be read increasing and the price of the tag goes up. And for each one of these frequencies has its own use and applications.10
- Methods a transponder is powered by 11
- For tags to be in effort, they need power even if power levels are very small and could be in a range of micro- to mille Watts. So tags can be passive, active, or semi-passive:12
- Active tags
- These kinds of tags require a power source; it could be a battery or a powered communications. And they are usually read/write devices with limited life time to the energy stored in it.
- Passive tags
- Passive tags do not require any source to power so they have no limit in their life and need no repairs beside they are small and practical.
- Semi-passive ( two- way tags)
- Those tags can be powered passively or by power supply, and they are bigger and more expensive than the passive ones.
- Data-carrying options
- To get the recovery wanted, some bits like error-detection bits and additions like data identifier need to be added in order to organize data stored in data carriers.13
- Data read rates
- Data transfer rate has been stated and it is linked to carrier frequency. Even if scaled in milliseconds, reading or transferring the data demands a finite period of time that can essentially be a matter in applications where a tag is passed rapidly through a reading zone.14
- Programming options
- It can be read-only, read/write or WORM devices and that will affect in the cost of it.
- Physical form
- RFID tags come in a broad physical forms, shapes, sizes, and protective accommodation or encapsulations.
- Costs
- Depending on the type and of course the quantity wanted, the price can range from less than a few dollars for extremely simple tags to over $100 for the larger and more complicated devices .Generally, low-frequency devices are less expensive than high- frequency devices, and passive tags are usually less expensive than active tags.15
The Reader/interrogator
Depending on the kind of tags used and the objective to be fulfilled, the reader can be relatively different in complexity,RFID reader is to select analogue signals; an outer power supply give power to transmit the radio waves that runs in a precise pace in a cable to hit a metal on the antenna, this antenna will give the same exact signal rate out in space at a certain frequency and wavelength. It is important to mention that the reader has a regular processor and a digital signal processor chip to control and deal with the flow of electricity, adjust the frequency and the amplitude of the wave.16
Another function to the reader is to listen to a response from the tag, by receiving and broadcasting analogue waves, then turn them into digital bits, and then transmit this digital information to useful information about the object.17
If the signal is duplicated data from repetitive transmission after it is being correctly received and decoded, algorithms might be used to determine and solve it and then directs the tag to end the transmition. This is known as the command response protocol and is used to get out of problems of reading many tags in a rapid time. This is called hands down polling.
In another technique called hands up polling; the reader looks for tags with specific identities and interrogating them in turns. This is known as contention management.18
Antennas
There is antenna in both the reader and the tag so they can send and receive radio waves. A few centimetre tags’ antenna attached to the chip is to receive signal and transmit it after a little modifying. Whereas the reader’s antenna ranges in size and it is placed to do the same functionality of the tag’s antenna.
In a passive tag, the current comes out of reader has to orthogonally hit the antenna; the purpose of this is to assure that the passive tag gets powered up appropriately.19
By deeply looking at the system, the reader has the control in generating an appropriate radio frequency field by its antenna. When a tag gets passed through radio frequency field, it gets activated and then sends the information that programmed into its memory back, the array of antennas, usually one to four antennas, receive this signal, decode it, and send the information to the computer system.20
Size, shape, angles of the antenna has an overall impact in its performance, so it is placed or shaped to couple with a radio frequency wave at any chance so that it can maximize its performance.21
The middleware
The middleware is a reader interface layer that link and bring together all what got collected of data components to move data from a single computer to a local computer networks or even a global ones; it links up the data that comes into the reader to a software systems, and it can present a consist interface between RFID system hardware operation and its data elements into a lot of business applications such as purchasing, sales, marketing..Etc 22
The massive amounts of data and information that comes from millions of tag readings while moving in a sully chain need to be tied to deal with this information. Besides that, the middleware has the capability to filter and smooth these data.23
Middleware includes four elements; first, reader and device management to allow users to organize, supervise, and communicate with the reader by sending commands through a an interface. Second, data management, it is to direct and sort the data that comes from the reader to right destinations, third, application integration that has some features such as messaging, directing, connectivity to supply chain management or warehouse management..Etc. finally, partner integration in trade like business to business integration.24
Collision-free channels 25
Avoiding the data collision at the receiver while passing multiple tags through the reader has to be done by using either binary tree or ALOHA slot algorithms. In binary tree algorithm and during transmission, when data packets collide, the reader determines and resolves each collision a bit at a time through using binary tree search since each tag contains an ID related to it, whereas in ALOHA algorithm and while many tags are sending data packets in random periods, if the data packets collide, these packets wait for random back-off time prior giving another try.
RFID Today and Tomorrow 26
Current RFID
There is a lot of application of RFID system that are being applied in many fields such as logistics, automotive sector, food industry, and ministry of defence. Here are some of examples:
- Security/ policing: in passports and criminal tracking.
- Retail: track and trace, and product recall and shrinkage.
- Healthcare: monitoring blood banking in Red Cross.
- Airline: packaging handling.
Future RFID
However the technology has been improving and we check and look in some of these future expectations:
- Smart appliances:
- By taking the advantage of RFID tags in clothing and food packaging, home appliances could be operated in more intricate manner. In washing machine, a proper wash cycle can be automatically chosen, like avoid damaging soft or delicate fabrics for example. Or you can get a warning that you are out of milk or yogurt has been expired from your refrigerator. And it could be more interesting when it could even automatically send shopping list to a home delivery service
- Shopping:
- Customers can just roll the shopping cart beyond the point- sale terminal when they want to check out, these terminals can automatically check, compute the total costs of the items in the cart, and it is interestingly can charge the customers by applying Merloni technology with RFID technology.
Merloni company has develop a prototype RFID-enabled payment devices and send receipts to mobile phones, so costumers do not have to have the receipts when they want to return items, since RFID tag has the history and the payment record of this item.
- Medication compliance:
- Intel and University of Washington research is to apply RFID to ease medication implementation and home routing for impaired and elderly people. For instance, RFID- enabled medicine cabinet can aid verifying that medications are taken in the right time.
Privacy implementation issues
Secret tracking and inventorying can be main concern about users’ privacy. Since the RFID tags just react to reader without holders’ awareness, so there is a realistic threat of secret scanning where read range authorized.27
Privacy threat rises when the tag is mutual with some personal information, For instance, if a purchase made by a credit card, the shop can link between the serial number in the tag and the identity of the consumer and then to the profile of card holder using some networks of RFID readers inside or outside the shop, even shop can use a wireless devices as Bluetooth enabled devices.28
Libraries, passports, human implanting are some of several areas of everyday life that privacy is a concern that RFID might threaten it if engineers cannot find a proper solution to stop that.
References
[1] Farid Dowla, Handbook of RF & wireless technologies,200 Wheeler Road,Burlington,USA,2004, Newnes.
[2] Meg Mcginity,“ RFID: is this game of tag fair play?”, portal,http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id =962097 ( Accessed Feb 28th 2008).
[3] Dowla, Hnadbook of RF & wireless technologies.
[4] Bhatt,Glover, RFID Essentials.
[5] Dowla, Hnadbook of RF & wireless technologies.
[6,7] Ibid.
[8] Rao, K.V.S.Intermec Technol. Corp, “An overview of backscattered radio frequency identifications system(RFID)”, http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/freeabs _all.jsp?arnumber=833700,( accessed in March 3rd,2008).
[9] Patrick J. Sweeney II, “RFID For Dummies”, Wiley Publishing, Inc.2005, PJ Sweeney - 2005 - media.wiley.com,(accessed Mar 2nd 2008).
[10] Hassan,T.and Chatterjee,S,” A Taxonomy for RFID.
[11,12] Sweeney II, RFID For Dummies.
[13,14,15] Dowla, Hnadbook of RF & wireless technologies.
[16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24] Sweeney II, RFID For Dummies.
[25] Engels, D.W. Sarma, S.E. The reader collision problem, Massachusetts Inst. of Technol., MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA,2002 ; http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=1176117.
[26] Engels., Sarma The reader collision problem.
[27] Want R, An introduction to RFID technology.
[28] Shepard, RFID Radio Frequency Identification.
See Also
External Links
Other Networks Topics other RFID
--Alhadds 10:35, 10 April 2009 (EDT)