AJAX Security
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
A full page is loaded only once when it is requested first time. Ajax engine, as an intermediate, takes the request for small segment of the page, which then requests information from the web server asynchronously. | A full page is loaded only once when it is requested first time. Ajax engine, as an intermediate, takes the request for small segment of the page, which then requests information from the web server asynchronously. | ||
| - | Ajax uses Javascript to make requests to the server using the XTTPRequest Object. The response is then handled by a Javascript method which processes and manipulates the data recieved from the server. | + | *Ajax uses Javascript to make requests to the server using the XTTPRequest Object. |
| + | *The response is then handled by a Javascript method which processes and manipulates the data recieved from the server. This can be done by the onreadystatechange method of the HTTPRequest Object. | ||
| + | *A request is made by the open() and send() method of the HTTPRequest Object in Javascript. | ||
| + | *The ''open() method'' is implemented using these parameters: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :First Parameter: | ||
| + | :Name of HTTP request method (GET, POST, HEAD etc.) | ||
| + | :Second Parameter: | ||
| + | :URL of the requested page to read data from. | ||
| + | :Third Parameter: | ||
| + | :A boolean value (TRUE, FALSE), to specify whether the request is asynchronous or synchronous. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *The ''send() method'' is sent with variables that are needed for the request in its parameters. | ||
| + | *The ''readyState'' property is used to check the state of the request. | ||
| + | *The ''status'' property is used to check the status of the HTTP server response. | ||
| + | *The response data can then be retrieved from ''responseText'' (returns data from server in plain text) or ''responseXML'' (returns data from server in XML format).[8] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| Line 59: | Line 78: | ||
==Types of Attacks on AJAX== | ==Types of Attacks on AJAX== | ||
| - | ===Cross Site Scripting=== | + | ===Cross-Site Scripting and Cross-Site Request Forgery=== |
| + | |||
| + | With un-validated user input being sent directly to the server | ||
One of the major concerns of attack that exploits AJAX through Cross Site Scripting. | One of the major concerns of attack that exploits AJAX through Cross Site Scripting. | ||
In case of cross-site scripting, maliciously injected scripts can actually leverage the AJAX provided functionalities to act on behalf of the user thereby tricking the user with the ultimate aim of redirecting his browsing session (e.g., phishing). | In case of cross-site scripting, maliciously injected scripts can actually leverage the AJAX provided functionalities to act on behalf of the user thereby tricking the user with the ultimate aim of redirecting his browsing session (e.g., phishing). | ||
Revision as of 01:03, 12 April 2009
AJAX stands for Asynchronous JavaScript And XML.AJAX is a type of programming, it is not a new type of technology, but instead, a combination of existing technologies used for a robust foundation for web application. These technologies include:[4]
- HTML and Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
- Document Object Model (DOM)
- XML
- XML HTTP Request
- JavaScript (JS)
The use of AJAX provides faster and more user friendly web applications than traditional web sites.
Contents |
Functionality
Traditional Process
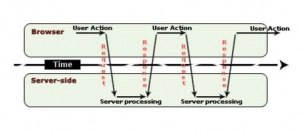
The process of tradition website function by the user making a request, and the browser sends the request to the appropriate server. The server generates the requested web page as a response and the data is sent to the client. This process is all done synchronously.[8]
How AJAX works
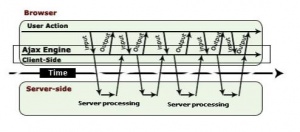
Ajax adds an extra layer of functionality in the communication model. Ajax engine acts as an intermediate between the user interaction to the browser and the server system. A full page is loaded only once when it is requested first time. Ajax engine, as an intermediate, takes the request for small segment of the page, which then requests information from the web server asynchronously.
- Ajax uses Javascript to make requests to the server using the XTTPRequest Object.
- The response is then handled by a Javascript method which processes and manipulates the data recieved from the server. This can be done by the onreadystatechange method of the HTTPRequest Object.
- A request is made by the open() and send() method of the HTTPRequest Object in Javascript.
- The open() method is implemented using these parameters:
- First Parameter:
- Name of HTTP request method (GET, POST, HEAD etc.)
- Second Parameter:
- URL of the requested page to read data from.
- Third Parameter:
- A boolean value (TRUE, FALSE), to specify whether the request is asynchronous or synchronous.
- The send() method is sent with variables that are needed for the request in its parameters.
- The readyState property is used to check the state of the request.
- The status property is used to check the status of the HTTP server response.
- The response data can then be retrieved from responseText (returns data from server in plain text) or responseXML (returns data from server in XML format).[8]
Advantages of AJAX
AJAX is used for being able to provide users with a greater web browsing experience due to faster and more interactivity compared to traditional web technologies.
Its main advantage is the use of the XML HTTP Request which allows a web page to refresh a small portion of its data from a web server(asynchronously), rather than being forced to reload and redraw the entire page as in traditional web programming. [5]
Current website using AJAX include Google Calender, GMail, Yahoo!, NetVibes.[6]
Security Vulnerabilities
Due to the increase popularity of AJAX and companies reliance of internet technology, web based applications have become more prone to attacks. Organizations must be prepared and secure themselves from the security risks.
By its nature, AJAX increases interactivity, it also allows for more network traffic which consequently increases the chance of attack that may not have been accessible with traditional technology.
AJAX technology is more of a white box application.The Ajax engine uses Javascript to capture the user commands and to transform them into function calls. Such function calls are not encrypted and sent in plain visible text to the server and may easily reveal important and private data which may be manipulated by a hacker.[4]
Although it is possible to obfuscate JavaScript, it only makes the code more difficult but not impossible for hackers to read.[3] With this information, a hacker can easily use AJAX functions without the intended interface by crafting specific HTTP requests directly to the server.[4]
Types of Attacks on AJAX
Cross-Site Scripting and Cross-Site Request Forgery
With un-validated user input being sent directly to the server One of the major concerns of attack that exploits AJAX through Cross Site Scripting. In case of cross-site scripting, maliciously injected scripts can actually leverage the AJAX provided functionalities to act on behalf of the user thereby tricking the user with the ultimate aim of redirecting his browsing session (e.g., phishing).
Example
The effect of MyLocalWeatherForecast.com’s shift to Ajax is that the client-side portion of the application (and by extension, the user) has more visibility into the server-side components.
See Also
References
External Links
Are AJAX Applications Vulnerable to Hack Attacks?
Testing for Security in the Age of AJAX Programming