Peer To Peer Network Security
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
'''Peer-to-Peer''' (or '''P2P''') networking is a fairly popular networking concept. Networks such as BitTorrent and eMule make it easy for people to find what they want and share what they have. P2P networks are used primarily to exchange pirated audio, video, software, and other inappropriate content. [5,6] | '''Peer-to-Peer''' (or '''P2P''') networking is a fairly popular networking concept. Networks such as BitTorrent and eMule make it easy for people to find what they want and share what they have. P2P networks are used primarily to exchange pirated audio, video, software, and other inappropriate content. [5,6] | ||
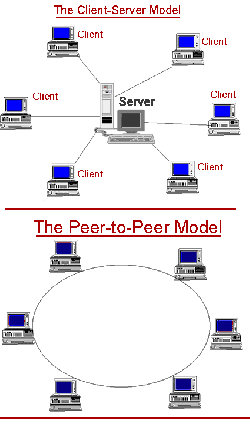
| + | [[Image:Peer_to_peer.gif|thumb|250px|right| The different between Client-Server and P2P model.[2]]] | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Network Structure== | ==Network Structure== | ||
| - | |||
Peer-to-peer file sharing networks are transient Internet networks that allow computer users with the same P2P networking program to connect with each other and use sophisticated searching techniques to directly access and download files from one another's hard drives. [7] | Peer-to-peer file sharing networks are transient Internet networks that allow computer users with the same P2P networking program to connect with each other and use sophisticated searching techniques to directly access and download files from one another's hard drives. [7] | ||
| + | The P2P overlay network consists of all the participating peers as network nodes. There are links between any two nodes that know each other. Based on how nodes link to each other, P2P networks can classify as '''Unstructured''' and '''Structured'''. [3] | ||
===Unstructured P2P networks=== | ===Unstructured P2P networks=== | ||
| + | An unstructured P2P network is formed when the overlay links are established arbitrarily. Such networks can be easily constructed as a new peer that wants to join the network can copy existing links of another node and then form its own links over time. In an unstructured P2P network, if a peer wants to find a desired piece of data in the network, the query has to be flooded through the network to find as many peers as possible that share the data. The main disadvantage with such networks is that the queries may not always be resolved. Popular content is likely to be available at several peers and any peer searching for it is likely to find the same thing, but if a peer is looking for rare data shared by only a few other peers, then it is highly unlikely that search will be successful. [3] | ||
===Structured P2P networks=== | ===Structured P2P networks=== | ||
| - | + | Structured P2P network employ a globally consistent protocol to ensure that any node can efficiently route a search to some peer that has the desired file, even if the file is extremely rare. Such a guarantee necessitates a more structured pattern of overlay links. By far the most common type of structured P2P network is the distributed hash table (DHT), in which a variant of consistent hashing is used to assign ownership of each file to a particular peer, in a way analogous to a traditional hash table's assignment of each key to a particular array slot. [3] | |
==Security Concern== | ==Security Concern== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 47: | ||
*[http://ntrg.cs.tcd.ie/undergrad/4ba2.02-03/p10.html P2P Security] | *[http://ntrg.cs.tcd.ie/undergrad/4ba2.02-03/p10.html P2P Security] | ||
| - | --[[User:Chowkw|Chowkw]] | + | ---- |
| + | Image:Architecture.png | ||
| + | |||
| + | --[[User:Chowkw|Chowkw]] 15:45, 7 April 2008 (EDT) | ||
Revision as of 19:46, 6 April 2008
Peer-to-Peer (or P2P) networking is a fairly popular networking concept. Networks such as BitTorrent and eMule make it easy for people to find what they want and share what they have. P2P networks are used primarily to exchange pirated audio, video, software, and other inappropriate content. [5,6]
Contents |
What is Peer to Peer Network
A pure peer-to-peer network does not have the notion of clients or servers, but only equal peer nodes that simultaneously function as both "clients" and "servers" to the other nodes on the network. A typical example for a non peer-to-peer file transfer is an FTP server where the client and server programs are quite distinct, and the clients initiate the download/uploads and the servers react to and satisfy these requests. [3] Besides file sharing, P2P networks are also used for Distributed Computation or Instant messaging.
Network Structure
Peer-to-peer file sharing networks are transient Internet networks that allow computer users with the same P2P networking program to connect with each other and use sophisticated searching techniques to directly access and download files from one another's hard drives. [7] The P2P overlay network consists of all the participating peers as network nodes. There are links between any two nodes that know each other. Based on how nodes link to each other, P2P networks can classify as Unstructured and Structured. [3]
Unstructured P2P networks
An unstructured P2P network is formed when the overlay links are established arbitrarily. Such networks can be easily constructed as a new peer that wants to join the network can copy existing links of another node and then form its own links over time. In an unstructured P2P network, if a peer wants to find a desired piece of data in the network, the query has to be flooded through the network to find as many peers as possible that share the data. The main disadvantage with such networks is that the queries may not always be resolved. Popular content is likely to be available at several peers and any peer searching for it is likely to find the same thing, but if a peer is looking for rare data shared by only a few other peers, then it is highly unlikely that search will be successful. [3]
Structured P2P networks
Structured P2P network employ a globally consistent protocol to ensure that any node can efficiently route a search to some peer that has the desired file, even if the file is extremely rare. Such a guarantee necessitates a more structured pattern of overlay links. By far the most common type of structured P2P network is the distributed hash table (DHT), in which a variant of consistent hashing is used to assign ownership of each file to a particular peer, in a way analogous to a traditional hash table's assignment of each key to a particular array slot. [3]
Security Concern
Applications
An important goal in peer-to-peer networks is that all clients provide resources, including bandwidth, storage space, and computing power. Thus, as nodes arrive and demand on the system increases, the total capacity of the system also increases. [3]
Peer-to-peer can be used for:
- File sharing
- Telephony
- Streaming media
- Software publication and distribution
References
- [1]http://www.spinellis.gr/pubs/jrnl/2004-ACMCS-p2p/html/AS04.html
- [2]http://www.ibiblio.org/team/intro/search/search.html
- [3]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peer-to-peer
- [4]http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/java/library/j-p2ptrust/
- [5]http://netsecurity.about.com/od/newsandeditorial1/a/p2psecurity.htm
- [6]http://www.websense.com/global/en/ResourceCenter/p2p_security.php
- [7]http://www.websense.com/docs/WhitePapers/PeertoPeer.pdf
See Also
External Links
Image:Architecture.png
--Chowkw 15:45, 7 April 2008 (EDT)