Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT)
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
| - | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DECT | + | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DECT Wikipedia: DECT] |
*[http://www.etsi.org/WebSite/Technologies/DECT.aspx DECT information at ETSI] | *[http://www.etsi.org/WebSite/Technologies/DECT.aspx DECT information at ETSI] | ||
*[http://www.dect.org/content.aspx?id=18 DECT Forum at dect.org] | *[http://www.dect.org/content.aspx?id=18 DECT Forum at dect.org] | ||
Revision as of 17:40, 11 April 2009
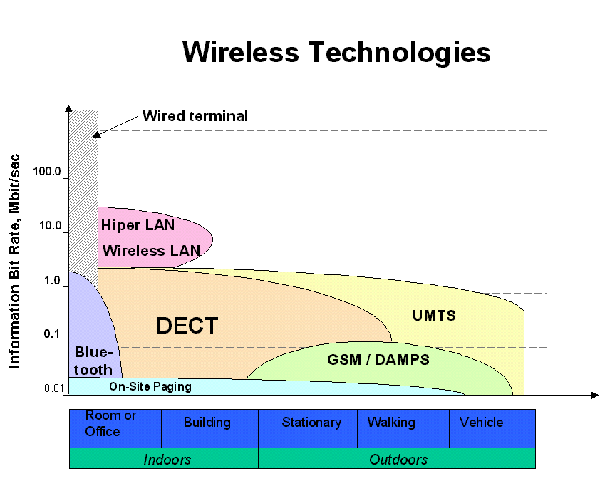
DECT or Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications is a radio standard for short-range cordless communications. It is commonly used for domestic or corporate purposes. It is suited to voice, data and networking applications with a range of up to 500 metres.
DECT was developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI); an independent, non-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe. Although DECT was developed by ETSI it has since been adopted by many countries all over the world.
While the original DECT frequency band is 1880 MHz - 1900 MHz, the frequency allocation has changed in some countries like the United States so that DECT devices can be sold there. Since these channels are reserved exclusively for voice communication applications, they are much less likely to experience interference from other wireless devices such as wireless networks or baby monitors. DECT devices are therefore known as being interference free.
Contents |
Applications
Features
Technical Details
References
- Prof. Dr. W. Kowalk (2007-03-13). Rechnernetze – DECT Retrieved on 2009-04-09. An introduction to DECT.
See also
External Links
--Colbyl2 17:32, 8 April 2009 (EDT)

