Domain Name System
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== History of DNS == | == History of DNS == | ||
| - | In the late 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA, later known as DARPA) funded and began working toward an internet technology called the ARPANET.<sup>[1]</sup> Each computer on the network was given an address for interconnecting with other computers on the network. In addition, this information was stored | + | In the late 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA, later known as DARPA) funded and began working toward an internet technology called the ARPANET.<sup>[1]</sup> Each computer on the network was given an address for interconnecting with other computers on the network. In addition, this information was stored on a central site, called the Network Information Center (NIC), in a single file named HOSTS.TXT.<sup>[3,4]</sup> Moreover, the HOSTS.TXT file contains information regarding the name-to-address mapping of all computers connected to the ARPANET.<sup>[3]</sup> Each computer on the network needed to retrieve this file in order to communication with other computers on the network. With only a small amount of computers interconnected at the start, HOSTS.TXT worked well. However, there are limitations with this scheme. If there is a change in the address in one of the computers on the network, every computer that want to communication with that machine would need to update its host file. Also, as the network traffic increases, there is a need to overcome problems such as overlapping names. As a result, DNS was invented to solve these limitations. |
The Domain Name System was invented by Jon Postel, Paul Mockapetris and Craig Partrige in 1983.<sup>[4]</sup> In addition, they published the original specification, RFC 882, for the DNS. Over the years, several more RFCs have been published to update the DNS specification, making the RFC 882 obsolete. | The Domain Name System was invented by Jon Postel, Paul Mockapetris and Craig Partrige in 1983.<sup>[4]</sup> In addition, they published the original specification, RFC 882, for the DNS. Over the years, several more RFCs have been published to update the DNS specification, making the RFC 882 obsolete. | ||
Revision as of 23:41, 9 April 2009
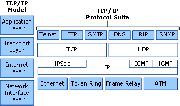
DNS is a hierarchical naming system used to map human-readable machine names into Internet Protocol addresses (IP addresses) for the Internet.[1] Although IP addresses provide a compact representation for identifying machines, users prefer to assign machines with pronounceable, meaningful, and easy-to-remember names.[1] DNS can be thought of as the Internet’s Phone Book. Instead of looking up a phone number using the person’s name or business’s name, the IP address can be looked up by using the domain name. For example, DNS translates the domain name www.mcmaster.ca into 130.113.64.65. DNS is also able to translate from IP addresses to domain names, which is known as Reverse Mapping or Inverse Mapping.[1]DNS is part of the Application Layer of the TCP/IP Internet Protocol Suite. It has two conceptually independent aspects. First, it specifies the name syntax and rules for delegating authority over names.[1] Secondly, it specifies the implementation of a system that efficiently maps names to addresses.[1]
Contents |
History of DNS
In the late 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA, later known as DARPA) funded and began working toward an internet technology called the ARPANET.[1] Each computer on the network was given an address for interconnecting with other computers on the network. In addition, this information was stored on a central site, called the Network Information Center (NIC), in a single file named HOSTS.TXT.[3,4] Moreover, the HOSTS.TXT file contains information regarding the name-to-address mapping of all computers connected to the ARPANET.[3] Each computer on the network needed to retrieve this file in order to communication with other computers on the network. With only a small amount of computers interconnected at the start, HOSTS.TXT worked well. However, there are limitations with this scheme. If there is a change in the address in one of the computers on the network, every computer that want to communication with that machine would need to update its host file. Also, as the network traffic increases, there is a need to overcome problems such as overlapping names. As a result, DNS was invented to solve these limitations.
The Domain Name System was invented by Jon Postel, Paul Mockapetris and Craig Partrige in 1983.[4] In addition, they published the original specification, RFC 882, for the DNS. Over the years, several more RFCs have been published to update the DNS specification, making the RFC 882 obsolete.
Name Syntax And Rules Of DNS
Delegation Of Authority For Names
Subset Authority
Top-Level Domains
Name Syntax And Type
Implementation of DNS
Mapping Domain Names To Addresses
Domain Name Resolution
Caching
Domain Name System Message Format
Abbreviation Of Domain Names
Security Concerns
Domain Registration
References
- Comer, D. E. (2006). The domain name system (DNS). Internetworking with TCP/IP (Fifth ed., pp. 419-441). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
- "What is DNS?: Domain Name System(DNS)". Retrieved on 2009-04-07
- "History of the Domain Name System". Retrieved on 2009-04-07.
- "History of Domain Name System". Retrieved on 2009-04-07.
See Also
External Links
--Jacky Ng (Ngck) 00:27, 8 April 2009 (EDT)