Ethernet Routing Devices
From Computing and Software Wiki
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
An '''Ethernet Switch''' works much like a Hub, but it is more selective of where to send received packets of data. Instead of transmitting the data to all connected NICs, a Switch reads the destination address and forwards the packet to that NIC only. This is accomplished using a routing table in the switch which keeps track of the connected IP addresses and the associated MAC addresses of the NICs. | An '''Ethernet Switch''' works much like a Hub, but it is more selective of where to send received packets of data. Instead of transmitting the data to all connected NICs, a Switch reads the destination address and forwards the packet to that NIC only. This is accomplished using a routing table in the switch which keeps track of the connected IP addresses and the associated MAC addresses of the NICs. | ||
| - | ===Advantages=== | + | ====Advantages==== |
* Lower probability of data collisions. Since data is only transmitted to the destination NIC, it is less likely that data will be leaving the NIC at the same time data is heading towards it. | * Lower probability of data collisions. Since data is only transmitted to the destination NIC, it is less likely that data will be leaving the NIC at the same time data is heading towards it. | ||
* A collision at one NIC does not affect the transmission of other NICs. | * A collision at one NIC does not affect the transmission of other NICs. | ||
* Attackers cannot affect switch configuration remotely | * Attackers cannot affect switch configuration remotely | ||
| - | ===Disadvantages=== | + | ====Disadvantages==== |
* Configuration changes require physical access to the switch. | * Configuration changes require physical access to the switch. | ||
* No firewall capabilities on the switch | * No firewall capabilities on the switch | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
===Ethernet Router=== | ===Ethernet Router=== | ||
| - | an '''Ethernet Router''' | + | an '''Ethernet Router''' is very similar to a Switch, with added functionality. Like a Switch, it reads the destination address of every incoming data packet and transmits it only to that NIC. Also like a Switch, a Router uses a routing table to accomplish this selective forwarding, storing the IP address and associated MAC address for each NIC. |
| + | |||
| + | Routers also have configuration software on them, allowing a user to configure the router settings remotely. Typically, a Router also has firewall software installed on it, which can also be configured remotely. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Advantages==== | ||
| + | * Low probability of data collisions due to data packets only being transmitted to a single NIC. | ||
| + | * Collisions at one NIC does not affect other NICs | ||
| + | * Remote configuration makes network administration easier | ||
| + | * Firewall software helps protect the network from outside threats, provided the router is the only link between the local network and external networks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Disadvantages==== | ||
| + | * More configuration required | ||
| + | * Firewall can cause problems in the network if configured incorrectly | ||
| + | * Attackers can attempt to gain access to the router, and if successful, take control of the network policies. | ||
| + | |||
| - | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| + | [http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Network_firewall Network Firewall]<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Network_Latency Network Latency]<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Onion_Routing Onion Routing]<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/IP_Spoofing IP Spoofing] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | [1] [http://www.tech-faq.com/ethernet-hub.shtml What is an Ethernet Hub?]<br> | ||
| + | [2] [http://compnetworking.about.com/library/advisor/blhomeadvisor_wiredrouter4.htm Build a Home Network]<br> | ||
| + | [3] [http://www.duxcw.com/faq/network/hubsw.htm What is the Difference Between a Hub and a Switch?] | ||
| + | |||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethernet Ethernet - Wikipedia] | ||
| + | |||
| + | --[[User:Kirbydm|Kirbydm]] 00:49, 5 April 2009 (EDT) | ||
Current revision as of 04:50, 5 April 2009
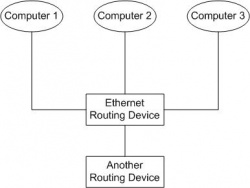
Ethernet Routing Devices are devices which enable complete connectivity between more then two hosts on an Ethernet network without any host requiring more than a single network interface card (NIC). Each NIC connects directly to the routing device which handles the flow of data on the network. Multiple routing devices can be connected together in the same way to create even larger Ethernet networks.Contents |
Types of Ethernet Routing Devices
Ethernet Hub
Ethernet Hubs work essentially like a shared bus. Every packet of data that enters the hub gets transmitted to all connected NICs.
Advantages
- No extra configuration needed. Just plug in the cables and it is ready to go.
Disadvantages
- Higher probability of data collisions. Since every packet of information is transmitted to each NIC, it is more likely that a packet of data leaving from the NIC will collide with a packet leaving the hub. This results in lost data and a lower overall transmission rate.
- When ever a collision occurs near any NIC, every host must stop transmitting to re-establish a collision free network state.
Ethernet Switch
An Ethernet Switch works much like a Hub, but it is more selective of where to send received packets of data. Instead of transmitting the data to all connected NICs, a Switch reads the destination address and forwards the packet to that NIC only. This is accomplished using a routing table in the switch which keeps track of the connected IP addresses and the associated MAC addresses of the NICs.
Advantages
- Lower probability of data collisions. Since data is only transmitted to the destination NIC, it is less likely that data will be leaving the NIC at the same time data is heading towards it.
- A collision at one NIC does not affect the transmission of other NICs.
- Attackers cannot affect switch configuration remotely
Disadvantages
- Configuration changes require physical access to the switch.
- No firewall capabilities on the switch
Ethernet Router
an Ethernet Router is very similar to a Switch, with added functionality. Like a Switch, it reads the destination address of every incoming data packet and transmits it only to that NIC. Also like a Switch, a Router uses a routing table to accomplish this selective forwarding, storing the IP address and associated MAC address for each NIC.
Routers also have configuration software on them, allowing a user to configure the router settings remotely. Typically, a Router also has firewall software installed on it, which can also be configured remotely.
Advantages
- Low probability of data collisions due to data packets only being transmitted to a single NIC.
- Collisions at one NIC does not affect other NICs
- Remote configuration makes network administration easier
- Firewall software helps protect the network from outside threats, provided the router is the only link between the local network and external networks.
Disadvantages
- More configuration required
- Firewall can cause problems in the network if configured incorrectly
- Attackers can attempt to gain access to the router, and if successful, take control of the network policies.
See Also
Network Firewall
Network Latency
Onion Routing
IP Spoofing
References
[1] What is an Ethernet Hub?
[2] Build a Home Network
[3] What is the Difference Between a Hub and a Switch?
External Links
--Kirbydm 00:49, 5 April 2009 (EDT)