Ethernet Routing Devices
From Computing and Software Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
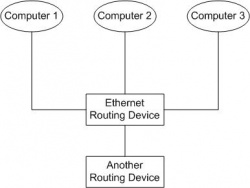
| - | '''Ethernet Routing Devices''' are devices which enable complete connectivity between more then two hosts on an Ethernet network without any host requiring more than a single network interface card (NIC). Each NIC connects directly to the routing device which handles the flow of data on the network. Multiple routing devices can be connected together in the same way to create even larger Ethernet networks. | + | [[Image:Network.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Ethernet Routing Device connecting a network]]'''Ethernet Routing Devices''' are devices which enable complete connectivity between more then two hosts on an Ethernet network without any host requiring more than a single network interface card (NIC). Each NIC connects directly to the routing device which handles the flow of data on the network. Multiple routing devices can be connected together in the same way to create even larger Ethernet networks. |
==Types of Ethernet Routing Devices== | ==Types of Ethernet Routing Devices== | ||
Revision as of 03:41, 5 April 2009
Ethernet Routing Devices are devices which enable complete connectivity between more then two hosts on an Ethernet network without any host requiring more than a single network interface card (NIC). Each NIC connects directly to the routing device which handles the flow of data on the network. Multiple routing devices can be connected together in the same way to create even larger Ethernet networks.Contents |
Types of Ethernet Routing Devices
Hub
Ethernet Hubs work essentially like a shared bus. Every packet of data that enters the hub gets transmitted to all connected NICs.
Advantages
- No extra configuration needed. Just plug in the cables and it is ready to go.
Disadvantages
- Higher probability of collisions. Since every packet of information is transmitted to each NIC, it is more likely that a packet of data leaving from the NIC will collide with a packet leaving the hub. This results in lost data and a lower overall transmission rate.