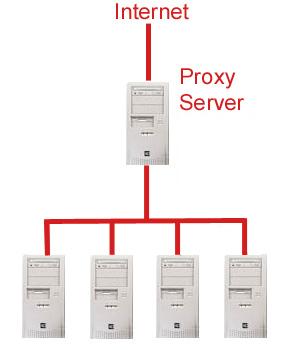
Proxy Server
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Proxyserver.jpg|thumb|350px|right|A '''proxy server''' acts as an intermediary between clients and other servers.]] | [[Image:Proxyserver.jpg|thumb|350px|right|A '''proxy server''' acts as an intermediary between clients and other servers.]] | ||
| - | A '''proxy server''' is a server that acts as a liaison between a client seeking resources and a server that can provide that resource. The client makes a request to the proxy, which then evaulates the request according to its pre-set filtering rules. If the request is validated, the proxy makes the request of the target server on behalf of the client and provides the resource to the client. Sometimes the proxy server may modify the client's request or the server's response based on the filtering rules, and may even contact a server different than the specified one in order to provide the requested resource. | + | A '''proxy server''' is a server that acts as a liaison between a client seeking resources and a server that can provide that resource. The client makes a request to the proxy, which then evaulates the request according to its pre-set filtering rules. If the request is validated, the proxy makes the request of the target server on behalf of the client and provides the resource to the client. Sometimes the proxy server may modify the client's request or the server's response based on the filtering rules, and may even contact a server different than the specified one in order to provide the requested resource. Proxies are used to ensure security, administrative control and caching services. |
| + | |||
| + | == Functionality == | ||
| + | A proxy server receives a request for a service (such as a Web page request) from a client. If it passes filtering requirements, the proxy server generally looks in its local cache of previously downloaded Web pages. If the page is found for example, the proxy returns it to the client without forwarding the request to the destination server. Otherwise, the proxy server acts as a client on behalf of the user and uses one of its own IP addresses to request the page from the server out on the Internet. When the page is returned, the proxy server relates it to the original request and forwards it on to the user. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To a user the proxy server is essentially non-existent; all Internet requests and returned responses appear to be directly with the addressed server. It should be noted however that the proxy is not necessarily invisible; its IP address has to be specified as a configuration option to the browser or other protocol. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An advantage of proxy servers is that all clients can theoretically access its cache. If one or more websites are frequently requested, these are likely to remain in the cache and improve response time. In fact, there are special proxy servers called cache servers. To this end, a proxy can also do logging. In addition, a proxy server can be separate or in the same machine as a firewall server and maintain the same functionality. | ||
== Types of Proxy Servers == | == Types of Proxy Servers == | ||
Revision as of 15:22, 11 March 2009
A proxy server is a server that acts as a liaison between a client seeking resources and a server that can provide that resource. The client makes a request to the proxy, which then evaulates the request according to its pre-set filtering rules. If the request is validated, the proxy makes the request of the target server on behalf of the client and provides the resource to the client. Sometimes the proxy server may modify the client's request or the server's response based on the filtering rules, and may even contact a server different than the specified one in order to provide the requested resource. Proxies are used to ensure security, administrative control and caching services.
Contents |
Functionality
A proxy server receives a request for a service (such as a Web page request) from a client. If it passes filtering requirements, the proxy server generally looks in its local cache of previously downloaded Web pages. If the page is found for example, the proxy returns it to the client without forwarding the request to the destination server. Otherwise, the proxy server acts as a client on behalf of the user and uses one of its own IP addresses to request the page from the server out on the Internet. When the page is returned, the proxy server relates it to the original request and forwards it on to the user.
To a user the proxy server is essentially non-existent; all Internet requests and returned responses appear to be directly with the addressed server. It should be noted however that the proxy is not necessarily invisible; its IP address has to be specified as a configuration option to the browser or other protocol.
An advantage of proxy servers is that all clients can theoretically access its cache. If one or more websites are frequently requested, these are likely to remain in the cache and improve response time. In fact, there are special proxy servers called cache servers. To this end, a proxy can also do logging. In addition, a proxy server can be separate or in the same machine as a firewall server and maintain the same functionality.
Types of Proxy Servers
There are many types of proxy servers that can act in different ways and provide similar but different functionality.