SSH Tunneling
From Computing and Software Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | Tunneling refers to a packet, which is based on one protocol, being wrapped, or encapsulated, in a second packet that is based on another protocol. The encapsulating packet's protocol will be whatever differing protocol is needed in order for it to travel over an intermediary network. An SSH tunnel is an encrypted network tunnel created using an SSH connection. This type of tunnel | + | Tunneling refers to a packet, which is based on one protocol, being wrapped, or encapsulated, in a second packet that is based on another protocol. The encapsulating packet's protocol will be whatever differing protocol is needed in order for it to travel over an intermediary network. An SSH tunnel is an encrypted network tunnel created using an SSH connection. This type of tunnel allows you to transmit otherwise insecure TCP traffic in a secure fashion, as well as transfer packets with incompatible protocols over an intermediary network. When a tunneling protocol uses data encryption (SSH) to transport packets that are based on insecure protocols over the Internet, they are in essence providing VPN functionality. |
== Components of a tunnel == | == Components of a tunnel == | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 9 April 2008
Tunneling refers to a packet, which is based on one protocol, being wrapped, or encapsulated, in a second packet that is based on another protocol. The encapsulating packet's protocol will be whatever differing protocol is needed in order for it to travel over an intermediary network. An SSH tunnel is an encrypted network tunnel created using an SSH connection. This type of tunnel allows you to transmit otherwise insecure TCP traffic in a secure fashion, as well as transfer packets with incompatible protocols over an intermediary network. When a tunneling protocol uses data encryption (SSH) to transport packets that are based on insecure protocols over the Internet, they are in essence providing VPN functionality.
Contents |
Components of a tunnel
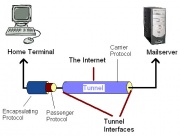
The Tunnel - The series of networks that the packet must travel to go from the starting network to the destination network.
Tunnel Interfaces - These are the points where the starting and destination networks comes into contact with the tunnel.
The Tunneling Process
In tunneling, a packet based on one protocol is wrapped, or encapsulated, in a second packet based on whatever differing protocol is needed in order for it to travel over an intermediary network. In effect, the second wrapper "insulates" the original packet and creates the illusion of a tunnel through which the wrapped packet travels across the intermediary network. In real-life terms, tunneling is comparable to "encapsulating" a present (the original packet) in a box (the secondary wrapper) for delivery through the postal system.
Applications
Implications???
History?
Refrences
See Also
External links
--Partsea 07:16, 9 April 2008 (EDT)