SOA enhancements through XML Networking
From Computing and Software Wiki
| (27 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)] enhancements through [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML Extensible Markup Language (XML)] Network''' has been a very discussed topic in the last few years. The performance and scalability of current SOA models are not sufficient to satisfy the increasing business demand of today's world. Web services for major companies are faced with extreme throughput issues that affect all the underlying applications that depend on such services. [http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/xml/library/x- | + | '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)] enhancements through [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML Extensible Markup Language (XML)] Network''' has been a very discussed topic in the last few years. The performance and scalability of current SOA models are not sufficient to satisfy the increasing business demand of today's world. Web services for major companies are faced with extreme throughput issues that affect all the underlying applications that depend on such services. [http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/xml/library/x-accsoa [1]] This wiki discusses the approaches that can be taken to accelerate this service-sharing process by expanding the use of XML technologies throughout the middleware of the SOA framekwork. [http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac147/archived_issues/ipj_9-4/xml_networking.html [2]] |
==SOA Overview== | ==SOA Overview== | ||
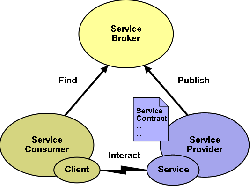
| - | [[Image:Soa_general_2.png|thumb|250px|right|Client and server interaction within a SOA framework. [http://www.w3.org/2003/Talks/0521-hh-wsa/slide5-0.html [8] ]]] | + | [[Image:Soa_general_2.png|thumb|250px|right|'''Figure 1''' <br> Client and server interaction within a SOA framework. [http://www.w3.org/2003/Talks/0521-hh-wsa/slide5-0.html [8] ]]] |
| - | The web services concept provides a framework for sharing services across a network (such as the internet). Each of these services represent a group of objects and resources that are combined to provide a tool for business applications. Service-oriented architectures use these tools to build applications: various services are grouped together to form the desired product. | + | The web services concept provides a framework for sharing services across a network (such as the internet). Each of these services represent a group of objects and resources that are combined to provide a tool for business applications. Service-oriented architectures use these tools to build their custom applications: various services are grouped together to form the desired product (see figure 1). Therefore naturally the key factor for the success of SOA is interoperability. This means that services must be reachable from within any development framework: Java SE, .NET, etc. For such concept to become true various standards and regulations must be specified. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture [3]] Such components will be discussed in the following section. |
===SOA Components=== | ===SOA Components=== | ||
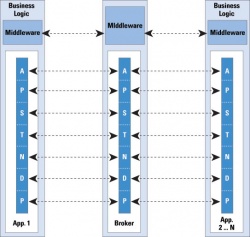
| - | [[Image:Soa_general.jpg|thumb|250px|right| | + | [[Image:Soa_general.jpg|thumb|250px|right|'''Figure 2''' <br> Network messaging layer of a common SOA framework. [http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac147/archived_issues/ipj_9-4/xml_networking.html [2] ]]] The main "ingredients" for a web service layer, and essentially a service-oriented architecture are: UDDI, WSDL, SOAP and HTTP. Together they specify what the web service is and how to reach it, which is all the client application needs to know. |
====UDDI==== | ====UDDI==== | ||
*Stands for Universal Description,Discovery and Integration. | *Stands for Universal Description,Discovery and Integration. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
*Allows for a communication channel between a client and a server. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP [7]] | *Allows for a communication channel between a client and a server. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP [7]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
==Enhancements through XML Networking== | ==Enhancements through XML Networking== | ||
| - | + | As noted above, all aspects of a service-oriented architecture are based on the XML standard. However it is strange to realize that a large number of existent SOA-based systems do not take advantage of the growing arsenal of XML-related technologies. [http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/xml/library/x-accsoa [1]] In its current framework state, a large incoming SOAP request can really damage the throughput of a network: this message needs to be de-serialized, then proper networking routing logic applied, serialized again, routed to the destination service, process the response, and finally build the outgoing SOAP envelope. The efficiency of all these steps can be improved by applying XML-related tools at the network level, and therefore avoid the penalty of serialization/de-serialization of large SOAP messages. [http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac147/archived_issues/ipj_9-4/xml_networking.html [2]] | |
===Overview of Technologies=== | ===Overview of Technologies=== | ||
| + | Below is a brief listing of the main XML technologies that can be utilized to enhance the networking of web services. | ||
====XSD==== | ====XSD==== | ||
| - | + | *XML Schema (XSD) is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web_Consortium W3C Standard] that specifies the rules and structure of its related instances. | |
| + | *Designed to replace [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_Type_Definition Document Type Definition (DTD)], allowing for more complex internal structures. | ||
| + | *Can improve performance of optimized parsers. [http://www.xml.com/pub/a/1999/12/dtd/index.html [9]] | ||
====XSLT==== | ====XSLT==== | ||
| + | *Stands for Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation. | ||
| + | *Transforms a given XML document into another document (usually XML or XHTML) based on content filtering and manipulation. | ||
| + | *Main goal is to make documents readable by humans. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XSL_Transformations [10]] | ||
====XPath==== | ====XPath==== | ||
| + | *Stands for XML Path Language. | ||
| + | *It allows for easy navigation of XML documents | ||
| + | *Values (string, booleans and numbers) can also be calculated from various nodes. | ||
| + | *In its newest version (2.0), an entire subtree can be returned as the result of a query. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XPath [11]] | ||
====XQuery==== | ====XQuery==== | ||
| + | *A query language for XML documents. | ||
| + | *Main goal is to make SQL-like queries. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XQuery [12]] | ||
====XML Encryption==== | ====XML Encryption==== | ||
| - | + | *Allows for encryption of specific elements within a document. | |
| + | *Speeds up the cryptographic process of documents. [http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlenc-core/ [13]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
===Integrating XML Network=== | ===Integrating XML Network=== | ||
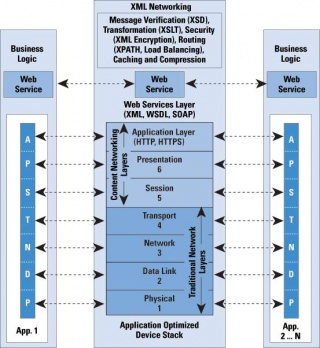
| - | [[Image:Soa_xml.jpg|thumb|320px| | + | [[Image:Soa_xml.jpg|thumb|320px|right|'''Figure 3''' <br>Integration of XML technologies inside a service-oriented architecture. [http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac147/archived_issues/ipj_9-4/xml_networking.html [2] ]]] |
| + | Now that the key XML technologies have been presented we can illustrate their integration and how they can improve the web services network by continuing to use the "large SOAP request" example. First of all, this message can be properly routed to its web server destination by using XPath to examine the message ''payload'' (instead of just the header). [http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac147/archived_issues/ipj_9-4/xml_networking.html [2]] <br><br> | ||
| - | + | Such "on the spot" content-based routing avoids a huge networking delay that was caused by serialization of the message in order to find where it should go. Also, with the help of a corresponding XML Schema this process can be further improved since the leading-market parsers now offer optimizations based on xsd documents. Continuing now at the data-retrieval level of the web service provider, XQuery (using XPath) can be utilized to perform efficient queries such as extracting an entire subtree from the database and placing it into the response message. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XQuery [12]]<br><br> | |
| - | + | In terms of encryption, the advantages of XML Encryption standards allow for precise element encryption, allowing sensitive networking information to be read in a very efficient manner. Lastly, the XSLT documents can avoid unnecessary network traffic by directly transforming XML documents into different formats without having to send to another service provider. <br><br> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Figure 3 illustrates the integration of an XML-enhanced web service network. The middle-layer now contains new technology that allows it to become more efficient and provide a much higher throughput of responses when faced with large quantity of requests from the client. | |
| - | |||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | ==FastSOA: the next step== | ||
| + | [[Image:Soa_fast.gif|thumb|650px|right|'''Figure 4''' <br>FastSOA concept integrated with a service-oriented architecture [http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/xml/library/x-accsoa/ [1] ]]] | ||
| + | As described in Frank Cohen's article [http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/xml/library/x-accsoa [1]], FastSOA is a concept that further extends the use of XML technologies to improve web services networking. The basic idea of FastSOA is to cache frequently requested information inside a native XML database (not a relational database). Therefore whenever this request is repeated, the web service provider can quickly use XQuery to extract the response and thus avoid the bandwidth of going through the original data retrieval process. <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Careful considerations had to be made when designing this new concept. Since many organizations already have a stable service-oriented framework in place, they would not be willing to implement an optimization that would disrupt the flow of data. That's the main reason for FastSOA's encapsulated layer, as seen in Figure 4. Basically, this new caching system becomes the first ''service'' that an incoming request goes through.<br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The real benefits, as illustrated by Cohen, cannot be seen if requests are completely different or occur in very long time intervals. However for extremely busy web service providers such as an international car parts manufactory, FastSOA extremely improves the networking delay between responses. This enhancement in bandwidth has sprung a very large interest in caching of frequent requests. Of course, this speedup is only possible with the aid of the mentioned XML-related technologies. Therefore we can conclude that in the next few years all existent service-oriented architectures will take the necessary steps to embrace these XML networking solutions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <br>'''1.''' Frank Cohen: [http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/xml/library/x-accsoa FastSOA: Accelerate SOA with XML, XQuery, and native XML database technology] IBM.com February 7, 2006. | ||
| + | <br>'''2.''' Silvano Da Ros: [http://www.cisco.com/web/about/ac123/ac147/archived_issues/ipj_9-4/xml_networking.html Boosting the SOA with XMLNetworking], Cisco.com December 1, 2006. | ||
| + | <br>'''3.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture Service-oriented architecture], Wikipedia April 6, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''4.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UDDI UDDI], Wikipedia March 25, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''5.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_Services_Description_Language WSDL], Wikipedia March 7, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''6.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOAP SOAP], Wikipedia April 3, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''7.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP HTTP], Wikipedia April 6, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''8.''' Hugo Haas [http://www.w3.org/2003/Talks/0521-hh-wsa/slide5-0.html SOA Diagram], W3C.org May 21, 2003. | ||
| + | <br>'''9.''' Simon St. Laurent: [http://www.xml.com/pub/a/1999/12/dtd/index.html Describing your Data: DTDs and XML Schemas], XML.com December 1, 1999. | ||
| + | <br>'''10.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XSL_Transformations XSLT], Wikipedia March 27, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''11.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XPath XPath], Wikipedia April 4, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''12.''' [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XQuery XQuery], Wikipedia March 27, 2008. | ||
| + | <br>'''13.''' [http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlenc-core/ XML Encryption], W3C December 10, 2002. | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| - | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML_Schema_%28W3C%29 The XML Schema Technology] | + | *Hao He: [http://webservices.xml.com/pub/a/ws/2003/09/30/soa.html What Is Service-Oriented Architecture], XML.com September 30, 2003 |
| - | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web_Consortium W3C Standard] | + | *W3C: [http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml XML Recommendation] |
| - | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_Type_Definition Document Type Definition (DTD)] | + | *W3C: [http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-1 Schema Recommendation] |
| - | *[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML Extensible Markup Language (XML)] | + | *W3C: [http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath20 XPath Recommendation] |
| - | * [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OASIS_%28organization%29 OASIS] | + | *W3C: [http://www.w3.org/TR/xquery XQuery Recommendation] |
| + | *W3C: [http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt XSLT Recommendation] | ||
| + | *Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML_Schema_%28W3C%29 The XML Schema Technology] | ||
| + | *Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Wide_Web_Consortium W3C Standard] | ||
| + | *Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_Type_Definition Document Type Definition (DTD)] | ||
| + | *Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML Extensible Markup Language (XML)] | ||
| + | *Wikipedia: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OASIS_%28organization%29 OASIS] | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| + | *[http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Network-Based_Software_Architectures Network-Based Software Architectures] | ||
| + | *[http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Peer_To_Peer_Network_Security Peer To Peer Network Security] | ||
| + | *[http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Digital_Signatures Digital Signatures] | ||
| + | *[http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/Public_Key_Encryption_Algorithms Public Key Encryption Algorithms] | ||
| + | *[http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/wiki/index.php/TCP/IP_Application_Development TCP/IP Application Development] | ||
==Signature== | ==Signature== | ||
| - | + | --[[User:Demagaal|Demagaal]] 23:48, 6 April 2008 (EDT) | |
Current revision as of 00:45, 8 April 2008
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) enhancements through Extensible Markup Language (XML) Network has been a very discussed topic in the last few years. The performance and scalability of current SOA models are not sufficient to satisfy the increasing business demand of today's world. Web services for major companies are faced with extreme throughput issues that affect all the underlying applications that depend on such services. [1] This wiki discusses the approaches that can be taken to accelerate this service-sharing process by expanding the use of XML technologies throughout the middleware of the SOA framekwork. [2]
Contents |
SOA Overview
The web services concept provides a framework for sharing services across a network (such as the internet). Each of these services represent a group of objects and resources that are combined to provide a tool for business applications. Service-oriented architectures use these tools to build their custom applications: various services are grouped together to form the desired product (see figure 1). Therefore naturally the key factor for the success of SOA is interoperability. This means that services must be reachable from within any development framework: Java SE, .NET, etc. For such concept to become true various standards and regulations must be specified. [3] Such components will be discussed in the following section.
SOA Components
The main "ingredients" for a web service layer, and essentially a service-oriented architecture are: UDDI, WSDL, SOAP and HTTP. Together they specify what the web service is and how to reach it, which is all the client application needs to know.UDDI
- Stands for Universal Description,Discovery and Integration.
- Sponsored by OASIS.
- An XML-based registry that allows businesses to list and search for web services. [4]
WSDL
- Stands for Web Services Description Language.
- An XML-based language that describes a web service.
- The 2.0 version is a W3C recommendation. [5]
SOAP
- Stands for Simple Object Access Protocol.
- A protocol for exchanging XML-based messages over a network.
- Provides a standard message format for services to use. [6]
HTTP
- Stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
- It is used to transfer information through a network (intranet, of world wide web).
- Allows for a communication channel between a client and a server. [7]
Enhancements through XML Networking
As noted above, all aspects of a service-oriented architecture are based on the XML standard. However it is strange to realize that a large number of existent SOA-based systems do not take advantage of the growing arsenal of XML-related technologies. [1] In its current framework state, a large incoming SOAP request can really damage the throughput of a network: this message needs to be de-serialized, then proper networking routing logic applied, serialized again, routed to the destination service, process the response, and finally build the outgoing SOAP envelope. The efficiency of all these steps can be improved by applying XML-related tools at the network level, and therefore avoid the penalty of serialization/de-serialization of large SOAP messages. [2]
Overview of Technologies
Below is a brief listing of the main XML technologies that can be utilized to enhance the networking of web services.
XSD
- XML Schema (XSD) is a W3C Standard that specifies the rules and structure of its related instances.
- Designed to replace Document Type Definition (DTD), allowing for more complex internal structures.
- Can improve performance of optimized parsers. [9]
XSLT
- Stands for Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformation.
- Transforms a given XML document into another document (usually XML or XHTML) based on content filtering and manipulation.
- Main goal is to make documents readable by humans. [10]
XPath
- Stands for XML Path Language.
- It allows for easy navigation of XML documents
- Values (string, booleans and numbers) can also be calculated from various nodes.
- In its newest version (2.0), an entire subtree can be returned as the result of a query. [11]
XQuery
- A query language for XML documents.
- Main goal is to make SQL-like queries. [12]
XML Encryption
- Allows for encryption of specific elements within a document.
- Speeds up the cryptographic process of documents. [13]
Integrating XML Network
Now that the key XML technologies have been presented we can illustrate their integration and how they can improve the web services network by continuing to use the "large SOAP request" example. First of all, this message can be properly routed to its web server destination by using XPath to examine the message payload (instead of just the header). [2]
Such "on the spot" content-based routing avoids a huge networking delay that was caused by serialization of the message in order to find where it should go. Also, with the help of a corresponding XML Schema this process can be further improved since the leading-market parsers now offer optimizations based on xsd documents. Continuing now at the data-retrieval level of the web service provider, XQuery (using XPath) can be utilized to perform efficient queries such as extracting an entire subtree from the database and placing it into the response message. [12]
In terms of encryption, the advantages of XML Encryption standards allow for precise element encryption, allowing sensitive networking information to be read in a very efficient manner. Lastly, the XSLT documents can avoid unnecessary network traffic by directly transforming XML documents into different formats without having to send to another service provider.
Figure 3 illustrates the integration of an XML-enhanced web service network. The middle-layer now contains new technology that allows it to become more efficient and provide a much higher throughput of responses when faced with large quantity of requests from the client.
FastSOA: the next step
As described in Frank Cohen's article [1], FastSOA is a concept that further extends the use of XML technologies to improve web services networking. The basic idea of FastSOA is to cache frequently requested information inside a native XML database (not a relational database). Therefore whenever this request is repeated, the web service provider can quickly use XQuery to extract the response and thus avoid the bandwidth of going through the original data retrieval process.
Careful considerations had to be made when designing this new concept. Since many organizations already have a stable service-oriented framework in place, they would not be willing to implement an optimization that would disrupt the flow of data. That's the main reason for FastSOA's encapsulated layer, as seen in Figure 4. Basically, this new caching system becomes the first service that an incoming request goes through.
The real benefits, as illustrated by Cohen, cannot be seen if requests are completely different or occur in very long time intervals. However for extremely busy web service providers such as an international car parts manufactory, FastSOA extremely improves the networking delay between responses. This enhancement in bandwidth has sprung a very large interest in caching of frequent requests. Of course, this speedup is only possible with the aid of the mentioned XML-related technologies. Therefore we can conclude that in the next few years all existent service-oriented architectures will take the necessary steps to embrace these XML networking solutions.
References
1. Frank Cohen: FastSOA: Accelerate SOA with XML, XQuery, and native XML database technology IBM.com February 7, 2006.
2. Silvano Da Ros: Boosting the SOA with XMLNetworking, Cisco.com December 1, 2006.
3. Service-oriented architecture, Wikipedia April 6, 2008.
4. UDDI, Wikipedia March 25, 2008.
5. WSDL, Wikipedia March 7, 2008.
6. SOAP, Wikipedia April 3, 2008.
7. HTTP, Wikipedia April 6, 2008.
8. Hugo Haas SOA Diagram, W3C.org May 21, 2003.
9. Simon St. Laurent: Describing your Data: DTDs and XML Schemas, XML.com December 1, 1999.
10. XSLT, Wikipedia March 27, 2008.
11. XPath, Wikipedia April 4, 2008.
12. XQuery, Wikipedia March 27, 2008.
13. XML Encryption, W3C December 10, 2002.
External Links
- Hao He: What Is Service-Oriented Architecture, XML.com September 30, 2003
- W3C: XML Recommendation
- W3C: Schema Recommendation
- W3C: XPath Recommendation
- W3C: XQuery Recommendation
- W3C: XSLT Recommendation
- Wikipedia: The XML Schema Technology
- Wikipedia: W3C Standard
- Wikipedia: Document Type Definition (DTD)
- Wikipedia: Extensible Markup Language (XML)
- Wikipedia: OASIS
See Also
- Network-Based Software Architectures
- Peer To Peer Network Security
- Digital Signatures
- Public Key Encryption Algorithms
- TCP/IP Application Development
Signature
--Demagaal 23:48, 6 April 2008 (EDT)